Tonabersat suppresses priming/activation of the NOD-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and decreases renal tubular epithelial-to-macrophage crosstalk in a model of diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 38970061
- PMCID: PMC11225428
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01728-1
Tonabersat suppresses priming/activation of the NOD-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and decreases renal tubular epithelial-to-macrophage crosstalk in a model of diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
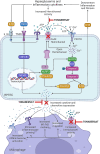
Background: Accompanied by activation of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, aberrant connexin 43 (Cx43) hemichannel-mediated ATP release is situated upstream of inflammasome assembly and inflammation and contributes to multiple secondary complications of diabetes and associated cardiometabolic comorbidities. Evidence suggests there may be a link between Cx43 hemichannel activity and inflammation in the diabetic kidney. The consequences of blocking tubular Cx43 hemichannel-mediated ATP release in priming/activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in a model of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) was investigated. We examined downstream markers of inflammation and the proinflammatory and chemoattractant role of the tubular secretome on macrophage recruitment and activation.
Methods: Analysis of human transcriptomic data from the Nephroseq repository correlated gene expression to renal function in DKD. Primary human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTECs) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) were cultured in high glucose and inflammatory cytokines as a model of DKD to assess Cx43 hemichannel activity, NLRP3 inflammasome activation and epithelial-to-macrophage paracrine-mediated crosstalk. Tonabersat assessed a role for Cx43 hemichannels.
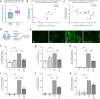
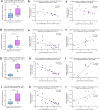
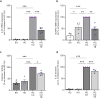
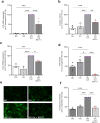
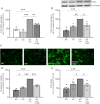
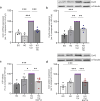
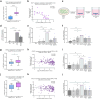
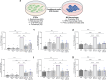
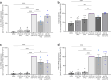
Results: Transcriptomic analysis from renal biopsies of patients with DKD showed that increased Cx43 and NLRP3 expression correlated with declining glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and increased proteinuria. In vitro, Tonabersat blocked glucose/cytokine-dependant increases in Cx43 hemichannel-mediated ATP release and reduced expression of inflammatory markers and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in RPTECs. We observed a reciprocal relationship in which NLRP3 activity exacerbated increased Cx43 expression and hemichannel-mediated ATP release, events driven by nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB)-mediated priming and Cx43 hemichannel opening, changes blocked by Tonabersat. Conditioned media (CM) from RPTECs treated with high glucose/cytokines increased expression of inflammatory markers in MDMs, an effect reduced when macrophages were pre-treated with Tonabersat. Co-culture using conditioned media from Tonabersat-treated RPTECs dampened macrophage inflammatory marker expression and reduced macrophage migration.
Conclusion: Using a model of DKD, we report for the first time that high glucose and inflammatory cytokines trigger aberrant Cx43 hemichannel activity, events that instigate NLRP3-induced inflammation in RPTECs and epithelial-to-macrophage crosstalk. Recapitulating observations previously reported in diabetic retinopathy, these data suggest that Cx43 hemichannel blockers (i.e., Tonabersat) may dampen multi-system damage observed in secondary complications of diabetes.
Keywords: Cell-cell communication; Connexin-43; Diabetic nephropathy; Hemichannel; Hyperglycaemia; Inflammasome; Inflammation; Macrophages; NLRP3; Tonabersat.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexin-43 hemichannels orchestrate NOD-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation and sterile inflammation in tubular injury.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 28;21(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01245-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37770948 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking connexin 43 hemichannel-mediated ATP release reduces communication within and between tubular epithelial cells and medullary fibroblasts in a model of diabetic nephropathy.Diabet Med. 2022 Dec;39(12):e14963. doi: 10.1111/dme.14963. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Diabet Med. 2022. PMID: 36256487 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of Yishen Jiangtang Decoction in regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome to improve renal damage in diabetic nephropathy db/db mice].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 May;50(10):2740-2749. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250114.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686143 Chinese.
-
Vitamin B and its derivatives for diabetic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 12;1(1):CD009403. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009403.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25579852 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review on urine albumin testing for early detection of diabetic complications.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Aug;9(30):iii-vi, xiii-163. doi: 10.3310/hta9300. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16095545
Cited by
-
Macrophages in Focus: Key Drivers and Therapeutic Opportunities in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jul 11;21(10):4647-4662. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.112737. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40765824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cardio-renal-metabolic role of the nod-like receptor protein-3 and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in early sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor therapy in people with diabetes who have had a myocardial infarction.Diabet Med. 2025 Jul;42(7):e70059. doi: 10.1111/dme.70059. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Diabet Med. 2025. PMID: 40281683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Double-Edged Effect of Connexins and Pannexins of Glial Cells in Central and Peripheral Nervous System After Nerve Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 1. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04991-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40310549 Review.
-
The role of intercellular communication in diabetic nephropathy.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1423784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423784. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39238645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexin 43 and Pannexin 1 hemichannels as endogenous regulators of innate immunity in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1523306. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1523306. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonnet F, Balkau B, Lambert O, Diawara Y, Combe C, Frimat L, et al. The number of nephroprotection targets attained is associated with cardiorenal outcomes and mortality in patients with diabetic kidney disease. The CKD-REIN cohort study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 doi: 10.1111/DOM.15507. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N/A/EFSD/Boehringer Ingelheim European Research Programme in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
- N/A/EFSD/Boehringer Ingelheim European Research Programme in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
- N/A/EFSD/Boehringer Ingelheim European Research Programme in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
- 18/0005919/DUK_/Diabetes UK/United Kingdom
- 18/0005919/DUK_/Diabetes UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

