Longitudinal plasma phosphorylated-tau217 and other related biomarkers in a non-demented Alzheimer's risk-enhanced sample
- PMID: 38970274
- PMCID: PMC11497664
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14100
Longitudinal plasma phosphorylated-tau217 and other related biomarkers in a non-demented Alzheimer's risk-enhanced sample
Abstract
Introduction: Understanding longitudinal change in key plasma biomarkers will aid in detecting presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: Serial plasma samples from 424 Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer's Prevention participants were analyzed for phosphorylated-tau217 (p-tau217; ALZpath) and other AD biomarkers, to study longitudinal trajectories in relation to disease, health factors, and cognitive decline. Of the participants, 18.6% with known amyloid status were amyloid positive (A+); 97.2% were cognitively unimpaired (CU).
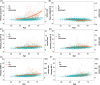
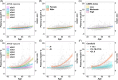
Results: In the CU, amyloid-negative (A-) subset, plasma p-tau217 levels increased modestly with age but were unaffected by body mass index and kidney function. In the whole sample, average p-tau217 change rates were higher in those who were A+ (e.g., simple slopes(se) for A+ and A- at age 60 were 0.232(0.028) and 0.038(0.013))). High baseline p-tau217 levels predicted faster preclinical cognitive decline.
Discussion: p-tau217 stands out among markers for its strong association with disease and cognitive decline, indicating its potential for early AD detection and monitoring progression.
Highlights: Phosphorylated-tau217 (p-tau217) trajectories were significantly different in people who were known to be amyloid positive. Subtle age-related trajectories were seen for all the plasma markers in amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired. Kidney function and body mass index were not associated with plasma p-tau217 trajectories. Higher plasma p-tau217 was associated with faster preclinical cognitive decline.
Keywords: ALZpath; BMI; biomarkers; cognitive composite; plasma; preclinical Alzheimer's disease.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
In the past 3 years, S.C.J. has served as consultant to Enigma, Prothena, and ALZpath. H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Alzecure, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). K.B. has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for AC Immune, Acumen, ALZPath, AriBio, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Lilly, Moleac Pte. Ltd, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served on data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials, and participated in educational programs for AC Immune, Biogen, Celdara Medical, Eisai, and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 860197/the Marie Skłodowska-Curie
- #2019-02397/the Swedish Research Council
- #ADSF-21-831377-C/the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- #2022-01018/the Swedish Research Council
- #201809-2016862/the Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA
- NIH
- R01 AG027161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- #ADSF-21-831381-C/the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- NIH RO1AG021155
- #ADSF-24-1284328-C/the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- the European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation
- R01 AG021155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #2023-00356/the Swedish Research Council
- R01AG027161
- RF1 AG027161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #ADSF-21-831376-C/the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- AARF
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

