Recent strides in macromolecular targeted photodynamic therapy for cancer
- PMID: 38971130
- PMCID: PMC11323206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102497
Recent strides in macromolecular targeted photodynamic therapy for cancer
Abstract
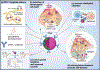
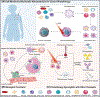
The recent approval of Akalux® for antibody-targeted photodynamic therapy (PDT) in Japan (also known as photoimmunotherapy), and the recent approval of Cytalux® for folate-specific image guided surgery by the FDA have motivated the continued development of macromolecular targeted PDT for cancer management. This review spotlights some of the most recent advances in macromolecular targeted PDT since 2021, exploring the latest advances in protein engineering, adaptive macromolecular constructs and nanotechnology, adoption of immune checkpoint inhibitors, and targeting using biomimetic membranes. These strategies summarized here attempt to expand the functionality, benefit, and success of macromolecular targeting for PDT to advance the technology beyond what has already entered into the clinical realm.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Strebhardt K & Ullrich A Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat Rev Cancer 8, 473–480 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Powers SK, Cush SS, Walstad DL & Kwock L Stereotactic intratumoral photodynamic therapy for recurrent malignant brain tumors. Neurosurgery 29, 688–696 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Mathe G, Ba LOCT & Bernard J Effect on mouse leukemia 1210 of a combination by diazo-reaction of amethopterin and gamma-globulins from hamsters inoculated with such leukemia by heterografts. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci 246, 1626–1628 (1958). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

