Probiotic evaluation, adherence capability and safety assessment of Lactococcus lactis strain isolated from an important herb "Murraya koenigii"
- PMID: 38971851
- PMCID: PMC11227525
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66597-7
Probiotic evaluation, adherence capability and safety assessment of Lactococcus lactis strain isolated from an important herb "Murraya koenigii"
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Probiotic evaluation, adherence capability and safety assessment of Lactococcus lactis strain isolated from an important herb "Murraya koenigii".Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 26;14(1):19769. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70191-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39187561 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
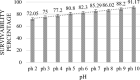
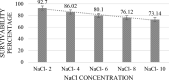
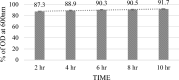
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from medicinal herb Murraya koenigii, commonly known as curry leaf, which promotes the growth and maintenance of gut microbiota, were studied for their probiotic potential. The key objective of this research was to isolate and evaluate probiotic characteristics, test adherence capabilities, and confirm their safety. Lactococcus lactis (MKL8), isolated from Murraya koenigii, was subjected to in vitro analysis to assess its resistance to the gastric environment, ability to adhere Caco-2 cells, anti-microbial activity, hydrophobicity, auto-aggregation, and safety profiling through MTT assay and hemolytic. MKL8 exhibited growth at 0.5% phenol concentrations (> 80%) and was able to survive in conditions with high bile concentrations (> 79%) and a relatively low pH (72%-91%). It shows high tolerance to high osmotic conditions (> 73%) and simulated gastric juice (> 72%). Additionally, MKL8 demonstrated strong hydrophobicity (85%), auto-aggregation (87.3%-91.7%), and adherence to Caco-2 cells. Moreover, it had an inhibitory effect against pathogens too. By performing the hemolytic and MTT assays, the non-toxicity of MKL8 isolate was examined, and it exhibited no harmful characteristics. Considering MKL8's resistance to gastrointestinal tract conditions, high surface hydrophobicity, non-toxicity, and ability to inhibit the tested pathogens, it can be concluded that MKL8 demonstrated promising probiotic properties and has potential for use in the food industry.
Keywords: Lactococcus lactis; Murraya koenigii; Adhesion ability; Antagonistic activity; Hydrophobicity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Antagonistic activity of recombinant Lactococcus lactis NZ1330 on the adhesion properties of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infection.Microb Pathog. 2019 Aug;133:103547. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103547. Epub 2019 May 18. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31112774
-
Characterization of two new strains of Lactococcus lactis for their probiotic efficacy over commercial synbiotics consortia.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Jun;53(2):903-920. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00685-6. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35138631 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, characterization of Weissella confusa and Lactococcus lactis from different milk sources and determination of probiotic features.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Mar;55(1):663-679. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-01208-7. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38158467 Free PMC article.
-
Functional probiotics of lactic acid bacteria from Hu sheep milk.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jul 28;20(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01920-6. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32723292 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Assessment of the Probiotic Potential of Lactococcus lactis LMG 7930 against Ruminant Mastitis-Causing Pathogens.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 9;12(1):e0169543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169543. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28068371 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of single and co-cultured lactic acid bacteria on antioxidant capacity and metabolite profiles during rambutan juice fermentation.Food Chem X. 2025 Aug 8;30:102904. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102904. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40831972 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic characteristics and whole genome sequencing of Pediococcus pentosaceus SNF15 and its protective effect on mice diarrhea induced by Escherichia coli K99.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 13;12:1524658. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1524658. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40151573 Free PMC article.
-
Survivability, antimicrobial and anticancer effects, and cytotoxicity of Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional Iranian cheese.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11344-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659782 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of bioactive properties and metabolomic profiling of probiotic bacteria Lactococcus lactis (MKL8).Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02327-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamont, J. R., Wilkins, O., Bywater-Ekegärd, M. & Smith, D. L. From yogurt to yield: Potential applications of lactic acid bacteria in plant production. Soil Biol. Biochem.111, 1–9 (2017). 10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.03.015 - DOI
-
- Chen, W. M., Tang, Y. Q., Mori, K. & Wu, X. L. Distribution of culturable endophytic bacteria in aquatic plants and their potential for bioremediation in polluted waters. Aquat. Biol.15(2), 99–110 (2012). 10.3354/ab00422 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

