Synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular docking, and MD simulation of novel 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors and antioxidant agents
- PMID: 38971857
- PMCID: PMC11227574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66424-z
Synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular docking, and MD simulation of novel 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors and antioxidant agents
Abstract
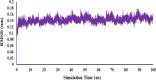
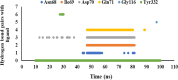
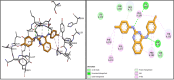
Alzheimer's disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder characterized by significant memory loss and cognitive impairments. Studies have shown that the expression level and activity of the butyrylcholinesterase enzyme increases significantly in the late stages of Alzheimer's disease, so butyrylcholinesterase can be considered as a promising therapeutic target for potential Alzheimer's treatments. In the present study, a novel series of 2,4-disubstituted quinazoline derivatives (6a-j) were synthesized and evaluated for their inhibitory activities against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinestrase (BuChE) enzymes, as well as for their antioxidant activities. The biological evaluation revealed that compounds 6f, 6h, and 6j showed potent inhibitory activities against eqBuChE, with IC50 values of 0.52, 6.74, and 3.65 µM, respectively. These potent compounds showed high selectivity for eqBuChE over eelAChE. The kinetic study demonstrated a mixed-type inhibition pattern for both enzymes, which revealed that the potent compounds might be able to bind to both the catalytic active site and peripheral anionic site of eelAChE and eqBuChE. In addition, molecular docking studies and molecular dynamic simulations indicated that potent compounds have favorable interactions with the active sites of BuChE. The antioxidant screening showed that compounds 6b, 6c, and 6j displayed superior scavenging capabilities compared to the other compounds. The obtained results suggest that compounds 6f, 6h, and 6j are promising lead compounds for the further development of new potent and selective BuChE inhibitors.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Cholinesterase inhibitors; MD simulation; Molecular docking; Quinazoline.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel deoxyvasicinone-indole as multi-target agents for Alzheimer's disease.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Oct 1;49:128212. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128212. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34153471
-
Unveiling piperazine-quinoline hybrids as potential multi-target directed anti-Alzheimer's agents: design, synthesis and biological evaluation.Mol Divers. 2025 Apr;29(2):1453-1478. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10927-4. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38990393
-
Novel pyridazinone derivatives as butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Nov;92:103304. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103304. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31561108
-
Synthesis of some new 3-coumaranone and coumarin derivatives as dual inhibitors of acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2013 Aug;346(8):577-87. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201300080. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2013. PMID: 23852709
-
Structure-based inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase with 2-Aryl-6-carboxamide benzoxazole derivatives: synthesis, enzymatic assay, and in silico studies.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb;29(1):671-693. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10828-6. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38554169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- George N, et al. Design, synthesis and in vitro biological activities of coumarin linked 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole hybrids as potential multi-target directed anti-Alzheimer agents. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022;34(4):101977. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101977. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

