Exploring the impacts of risk factors on mortality patterns of global Alzheimer's disease and related dementias from 1990 to 2021
- PMID: 38971870
- PMCID: PMC11227499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65887-4
Exploring the impacts of risk factors on mortality patterns of global Alzheimer's disease and related dementias from 1990 to 2021
Abstract
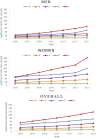
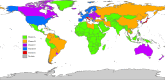
Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias (ADRD) affect millions of people worldwide, with mortality rates influenced by several risk factors and exhibiting significant heterogeneity across geographical regions. This study aimed to investigate the impact of risk factors on global ADRD mortality patterns from 1990 to 2021, utilizing clustering and modeling techniques. Data on ADRD mortality rates, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes prevalence were obtained for 204 countries from the GBD platform. Additional variables such as HDI, life expectancy, alcohol consumption, and tobacco use prevalence were sourced from the UNDP and WHO. All the data were extracted for men, women, and the overall population. Longitudinal k-means clustering and generalized estimating equations were applied for data analysis. The findings revealed that cardiovascular disease had significant positive effects of 1.84, 3.94, and 4.70 on men, women, and the overall ADRD mortality rates, respectively. Tobacco showed positive effects of 0.92, 0.13, and 0.39, while alcohol consumption had negative effects of - 0.59, - 9.92, and - 2.32, on men, women, and the overall ADRD mortality rates, respectively. The countries were classified into five distinct subgroups. Overall, cardiovascular disease and tobacco use were associated with increased ADRD mortality rates, while moderate alcohol consumption exhibited a protective effect. Notably, tobacco use showed a protective effect in cluster A, as did alcohol consumption in cluster B. The effects of risk factors on ADRD mortality rates varied among the clusters, highlighting the need for further investigation into the underlying causal factors.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Clustering; Dementia; Generalized estimating equations (GEE); Longitudinal k-means clustering.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar A, Sidhu J, Goyal A, Tsao JW. StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023) StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2023.
-
- Nichols E, Vos T. The estimation of the global prevalence of dementia from 1990–2019 and forecasted prevalence through 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 2019. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17:e051496. doi: 10.1002/alz.051496. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical