Artificial intelligence detects awareness of functional relation with the environment in 3 month old babies
- PMID: 38971875
- PMCID: PMC11227524
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66312-6
Artificial intelligence detects awareness of functional relation with the environment in 3 month old babies
Abstract
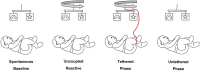
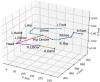
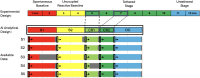
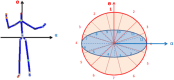
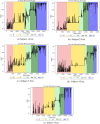
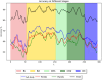
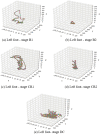
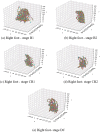
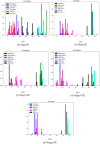
A recent experiment probed how purposeful action emerges in early life by manipulating infants' functional connection to an object in the environment (i.e., tethering an infant's foot to a colorful mobile). Vicon motion capture data from multiple infant joints were used here to create Histograms of Joint Displacements (HJDs) to generate pose-based descriptors for 3D infant spatial trajectories. Using HJDs as inputs, machine and deep learning systems were tasked with classifying the experimental state from which snippets of movement data were sampled. The architectures tested included k-Nearest Neighbour (kNN), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Fully connected network (FCNet), 1D-Convolutional Neural Network (1D-Conv), 1D-Capsule Network (1D-CapsNet), 2D-Conv and 2D-CapsNet. Sliding window scenarios were used for temporal analysis to search for topological changes in infant movement related to functional context. kNN and LDA achieved higher classification accuracy with single joint features, while deep learning approaches, particularly 2D-CapsNet, achieved higher accuracy on full-body features. For each AI architecture tested, measures of foot activity displayed the most distinct and coherent pattern alterations across different experimental stages (reflected in the highest classification accuracy rate), indicating that interaction with the world impacts the infant behaviour most at the site of organism~world connection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Turing A. Intelligent machinery. B. Jack Copeland. 2004;395:63.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

