Development and validation of a clinical nomogram to predict prostatic inflammation in men with lower urinary tract symptoms
- PMID: 38971935
- PMCID: PMC12106073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41391-024-00857-5
Development and validation of a clinical nomogram to predict prostatic inflammation in men with lower urinary tract symptoms
Abstract
Background: Prostatic inflammation is an important etiological component of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). The Prostatic Inflammation Nomogram Study (PINS) aimed to develop and validate a nomogram for predicting the presence of prostatic inflammation in men with LUTS.
Methods: This non-interventional, cross-sectional, prospective study was conducted in six secondary/tertiary centers across Cyprus, Greece, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. Men (≥40 years) with BPH/LUTS scheduled to undergo prostatic surgery or transrectal ultrasound-guided (TRUS) prostate biopsy were included. Fifteen demographic and clinical participant characteristics were selected as possible predictors of prostatic inflammation. The presence of inflammation (according to Irani score) in the prostatic tissue samples obtained from surgery/TRUS biopsy was determined. The effect of each characteristic on the likelihood a prostate specimen demonstrated inflammation (classified by Irani score into two categories, 0-2 [no/minimal inflammation] or 3-6 [moderate/severe inflammation]) was assessed using multiple logistic regression. A nomogram was developed and its discriminatory ability and validity were assessed.
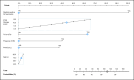
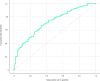
Results: In total, 423 patients (mean age 68.9 years) were recruited. Prostate volume ultrasound (PVUS) > 50 mL, history of urinary tract infection (UTI) treatment, presence of diabetes, and International Prostate Symptom Score (IPPS) Storage score were statistically significant predictors of Irani classification. Logistic regression demonstrated a statistically significant effect for leucocytes detected via urine dipstick, presence of diabetes, PVUS > 50 mL, history of UTIs, and higher IPSS Storage score for the odds of an inflammatory score category of 3-6 versus 0-2. The nomogram had a concordance index of 0.71, and good internal validity.
Conclusions: The nomogram developed from PINS had good predictive ability and identified various characteristics to be predictors of prostatic inflammation. Use of the nomogram may aid in individualizing treatment for LUTS, by identifying individuals who are candidates for therapies targeting prostatic inflammation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: This work was supported by research funding from Pierre Fabre. Stavros Gravas has received honoraria from GSK and Astellas. Cosimo De Nunzio is Editor-in-Chief of Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prostatic arterial embolization for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 29;3(3):CD012867. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012867.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35349161 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive treatments for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 15;7(7):CD013656. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013656.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693990 Free PMC article.
-
Silodosin for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012615. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012615.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29161773 Free PMC article.
-
Non-inferiority, randomised, open-label clinical trial on the effectiveness of transurethral microwave thermotherapy compared to prostatic artery embolisation in reducing severe lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: study protocol for the TUMT-PAE-1 trial.Trials. 2024 Sep 2;25(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08409-x. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39223593 Free PMC article.
-
Tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD002081. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002081. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Sep 07;(9):CD002081. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002081.pub2. PMID: 12535426 Updated.
Cited by
-
The Novel Histological Prostatic Inflammation Score Helps Defining the Association Between Stromal and Glandular Inflammation with the Risk of Prostate Cancer at Prostate Biopsy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;15(2):166. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15020166. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857050 Free PMC article.
-
The times have changed. Let the urologists change!Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025 Jun;28(2):243-244. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00828-w. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. PMID: 38575746 No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of Peri-Operative Outcomes after Prostatic Urethral Lift with Emphasis on Urodynamic Changes, Symptom Improvement and Sexual Function.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;14(19):2110. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192110. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39410516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bostanci Y, Kazzazi A, Momtahen S, Laze J, Djavan B. Correlation between benign prostatic hyperplasia and inflammation. Curr Opin Urol. 2013;23:5–10. - PubMed
-
- De Nunzio C, Presicce F, Tubaro A. Inflammatory mediators in the development and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Nat Rev Urol. 2016;13:613–26. - PubMed
-
- Samarinas M, Gacci M, de la Taille A, Gravas S. Prostatic inflammation: a potential treatment target for male LUTS due to benign prostatic obstruction. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018;21:161–7. - PubMed
-
- De Nunzio C, Kramer G, Marberger M, Montironi R, Nelson W, Schroder F, et al. The controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: the role of inflammation. Eur Urol. 2011;60:106–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical