How to update esophageal masses imaging using literature review (MRI and CT features)
- PMID: 38971944
- PMCID: PMC11227487
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-024-01754-0
How to update esophageal masses imaging using literature review (MRI and CT features)
Abstract
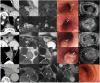
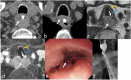
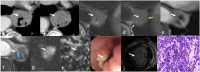
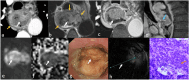
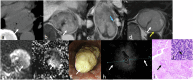
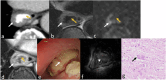
MRI offers new opportunities for detailed visualization of the different layers of the esophageal wall, as well as early detection and accurate characterization of esophageal lesions. Staging of esophageal tumors including extramural extent of disease, and status of the adjacent organ can also be performed by MRI with higher accuracy compared to other imaging modalities including CT and esophageal endoscopy. Although MDCT appears to be the primary imaging modality that is indicated for preoperative staging of esophageal cancer to assess tumor resectability, MDCT is considered less accurate in T staging. This review aims to update radiologists about emerging imaging techniques and the imaging features of various esophageal masses, emphasizing the imaging features that differentiate between esophageal masses, demonstrating the critical role of MRI in esophageal masses. CRITICAL RELEVANCE STATEMENT: MRI features may help differentiate mucosal high-grade neoplasia from early invasive squamous cell cancer of the esophagus, also esophageal GISTs from leiomyomas, and esophageal malignant melanoma has typical MR features. KEY POINTS: MRI can accurately visualize different layers of the esophagus potentially has a role in T staging. MR may accurately delineate esophageal fistulae, especially small mediastinal fistulae. MRI features of various esophageal masses are helpful in the differentiation.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Esophageal neoplasms; Magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.Y.W. is an employee of MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers. The remaining authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
References
-
- Lee SL, Yadav P, Starekova J et al (2021) Diagnostic performance of MRI for esophageal carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 299:583–594. 10.1148/radiol.2021202857 - PubMed
-
- Zhao K, Chu F, Wang Z et al (2023) Aorta and tracheobronchial invasion in esophageal cancer: comparing diagnostic performance of 3.0-T MRI and CT. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-023-09425-2 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

