Crosstalk between RNA m6A modification and epigenetic factors in plant gene regulation
- PMID: 38971972
- PMCID: PMC11573915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101037
Crosstalk between RNA m6A modification and epigenetic factors in plant gene regulation
Abstract
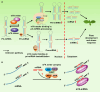
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant modification observed in eukaryotic mRNAs. Advances in transcriptome-wide m6A mapping and sequencing technologies have enabled the identification of several conserved motifs in plants, including the RRACH (R = A/G and H = A/C/U) and UGUAW (W = U or A) motifs. However, the mechanisms underlying deposition of m6A marks at specific positions in the conserved motifs of individual transcripts remain to be clarified. Evidence from plant and animal studies suggests that m6A writer or eraser components are recruited to specific genomic loci through interactions with particular transcription factors, 5-methylcytosine DNA methylation marks, and histone marks. In addition, recent studies in animal cells have shown that microRNAs play a role in depositing m6A marks at specific sites in transcripts through a base-pairing mechanism. m6A also affects the biogenesis and function of chromatin-associated regulatory RNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Although we have less of an understanding of the link between m6A modification and epigenetic factors in plants than in animals, recent progress in identifying the proteins that interact with m6A writer or eraser components has provided insights into the crosstalk between m6A modification and epigenetic factors, which plays a crucial role in transcript-specific methylation and regulation of m6A in plants.
Keywords: DNA methylation; RNA methylation; epigenetics; histone modification; long noncoding RNA; microRNA.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Amara U., Hu J., Park S.J., Kang H. ECT12, an YTH-domain protein, is a potential mRNA m6A reader that affects abiotic stress responses by modulating mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024;206:108255. - PubMed
-
- Amara U., Shoaib Y., Kang H. ALKBH9C, a potential RNA m6A demethylase, regulates the response of Arabidopsis to abiotic stresses and abscisic acid. Plant Cell Environ. 2022;45:3566–3581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

