Effective Management of Severe Amlodipine/Atenolol Overdose with Intravenous Calcium, Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemia Therapy, and Continuous Veno-Venous Hemodialysis: A Case Report
- PMID: 38973145
- PMCID: PMC11318701
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943777
Effective Management of Severe Amlodipine/Atenolol Overdose with Intravenous Calcium, Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemia Therapy, and Continuous Veno-Venous Hemodialysis: A Case Report
Abstract
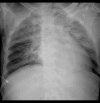
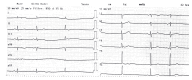
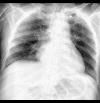
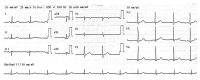
BACKGROUND Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, and atenolol, a beta blocker, are commonly used as a fixed drug combination (FDC) to treat hypertension. Intentional or non-intentional overdose of amlodipine-atenolol results in hypotension and myocardial depression with a high risk of mortality. This report describes a 64-year-old man with an overdose of amlodipine-atenolol, presenting as an emergency with hypotension, bradycardia, and severe metabolic acidosis. He was successfully treated with intravenous calcium chloride infusion, hyperinsulinemia euglycemia therapy (HIE), and continuous veno-venous hemodialysis (CVVHD). CASE REPORT A 64-year-old man was diagnosed with essential hypertension 1 week prior to the admission. He had been prescribed 1 FDC tablet of amlodipine and atenolol (5+50 mg) per day; however, he took 1 table of the FDC per day for 3 days and then took 3-4 tablets each day during the next 4 days. He was brought to the hospital with hypotension, bradycardia, and severe metabolic acidosis and was diagnosed with amlodipine-atenolol overdose. He was treated with intravenous calcium chloride infusion, HIE, and CVVHD. His hemodynamics started to improve after administering these therapies for 6 h. Inotropes were gradually tapered off and stopped. He was extubated on day 5 and recovered completely. CONCLUSIONS This report shows the serious effects amlodipine-atenolol overdose and the challenges of emergency patient management. An overdose of FDC of amlodipine and atenolol can cause cardiovascular collapse and severe metabolic acidosis. Timely and aggressive management with intravenous calcium infusion, HIE, and CVVHD is essential.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Case of Life-threatening Amlodipine and Atenolol Overdose.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):281-283. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23181. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31435148 Free PMC article.
-
Mixed amlodipine/valsartan overdose treated by the molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS™).Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2015 Jul;53(6):573-7. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1050594. Epub 2015 May 26. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2015. PMID: 26006182
-
Severe amlodipine intoxication treated by hyperinsulinemia euglycemia therapy.J Emerg Med. 2010 Jan;38(1):33-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.11.077. Epub 2008 Jul 26. J Emerg Med. 2010. PMID: 18657931
-
L-Carnitine for the treatment of a calcium channel blocker and metformin poisoning.J Med Toxicol. 2013 Sep;9(3):266-9. doi: 10.1007/s13181-013-0301-3. J Med Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23636657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment for beta-blocker poisoning: a systematic review.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020 Oct;58(10):943-983. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2020.1752918. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020. PMID: 32310006
Cited by
-
Advances in Understanding Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression and the Mechanisms of Acupuncture Intervention.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 27;17:5593-5609. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S490049. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39619130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeWitt CR, Waksman JC. Pharmacology, pathophysiology and management of calcium channel blocker and beta-blocker toxicity. Toxicol Rev. 2004;23(4):223–38. - PubMed
-
- Wong A, Hoffman RS, Walsh SJ, et al. Extracorporeal treatment for calcium channel blocker poisoning: Systematic review and recommendations from the EXTRIP workgroup. Clin Toxicol Phila Pa. 2021;59(5):361–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources