Evaluation of sodium borocaptate (BSH) and boronophenylalanine (BPA) as boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy (NCT) of cancer: an update and a guide for the future clinical evaluation of new boron delivery agents for NCT
- PMID: 38973634
- PMCID: PMC11337926
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12582
Evaluation of sodium borocaptate (BSH) and boronophenylalanine (BPA) as boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy (NCT) of cancer: an update and a guide for the future clinical evaluation of new boron delivery agents for NCT
Abstract
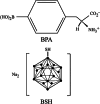
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a cancer treatment modality based on the nuclear capture and fission reactions that occur when boron-10, a stable isotope, is irradiated with neutrons of the appropriate energy to produce boron-11 in an unstable form, which undergoes instantaneous nuclear fission to produce high-energy, tumoricidal alpha particles. The primary purpose of this review is to provide an update on the first drug used clinically, sodium borocaptate (BSH), by the Japanese neurosurgeon Hiroshi Hatanaka to treat patients with brain tumors and the second drug, boronophenylalanine (BPA), which first was used clinically by the Japanese dermatologist Yutaka Mishima to treat patients with cutaneous melanomas. Subsequently, BPA has become the primary drug used as a boron delivery agent to treat patients with several types of cancers, specifically brain tumors and recurrent tumors of the head and neck region. The focus of this review will be on the initial studies that were carried out to define the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of BSH and BPA and their biodistribution in tumor and normal tissues following administration to patients with high-grade gliomas and their subsequent clinical use to treat patients with high-grade gliomas. First, we will summarize the studies that were carried out in Japan with BSH and subsequently at our own institution, The Ohio State University, and those of several other groups. Second, we will describe studies carried out in Japan with BPA and then in the United States that have led to its use as the primary drug that is being used clinically for BNCT. Third, although there have been intense efforts to develop new and better boron delivery agents for BNCT, none of these have yet been evaluated clinically. The present report will provide a guide to the future clinical evaluation of new boron delivery agents prior to their clinical use for BNCT.
Keywords: Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT); boronophenylalanine (BPA); brain tumors; head and neck cancer; sodium borocaptate (BSH).
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Sun Yat‐sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hatanaka H, Amano K, Kamano S, Sano K. Clinical experience of boron‐neutron capture therapy for malignant brain tumors (1968 ‐ 1985). In: Hatanaka H, editor. Boron neutron capture therapy for tumors. Japan: Nishimura Niigata; 1986:447–449.
-
- Hatanaka H, Kamano S, Amano K, Hojo S, Sano K, Egawa S, et al. Clinical experience of boron‐neutron capture therapy for gliomas‐a comparison with conventional chemo‐immuno‐radiotherapy. In: Hatanaka H, editor. Boron neutron capture therapy for tumors. Japan: Nishimura Niigata; 1986:349–378.
-
- Mishima Y, Honda C, Ichihashi M, Obara H, Hiratsuka J, Fukuda H, et al. Treatment of malignant melanoma by single thermal neutron capture therapy with melanoma‐seeking 10B‐compound. Lancet. 1989;2(8659):388–389. - PubMed
-
- Chanana AD, Capala J, Chadha M, Coderre JA, Diaz AZ, Elowitz EH, et al. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: interim results from the phase I/II dose‐escalation studies. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(6):1182–1192; discussion 92‐3. - PubMed
-
- Kato I, Fujita Y, Maruhashi A, Kumada H, Ohmae M, Kirihata M, et al. Effectiveness of boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent head and neck malignancies. Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 2009;67(7, Supplement):S37–S42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

