Expanding RNAi to Kidneys, Lungs, and Spleen via Selective ORgan Targeting (SORT) siRNA Lipid Nanoparticles
- PMID: 38973655
- PMCID: PMC11823468
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202313791
Expanding RNAi to Kidneys, Lungs, and Spleen via Selective ORgan Targeting (SORT) siRNA Lipid Nanoparticles
Abstract
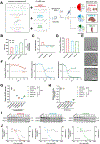
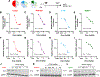
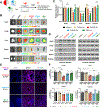
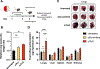
Inhibition of disease-causing mutations using RNA interference (RNAi) has resulted in clinically approved medicines with additional candidates in late stage trials. However, targetable tissues currently in preclinical development are limited to liver following systemic intravenous (IV) administration because predictable delivery of siRNA to non-liver tissues remains an unsolved challenge. Here, evidence of durable extrahepatic gene silencing enabled by siRNA Selective ORgan Targeting lipid nanoparticles (siRNA SORT LNPs) to the kidneys, lungs, and spleen is provided. LNPs excel at dose-dependent silencing of tissue-enriched endogenous targets resulting in 60%-80% maximal knockdown after a single IV injection and up to 88% downregulation of protein expression in mouse lungs after two doses. To examine knockdown potency and unbiased organ targeting, B6.129TdTom/EGFP mice that constitutively express the TdTomato transgene across all cell types are utilized to demonstrate 58%, 45%, and 15% reduction in TdTomato fluorescence in lungs, spleen, and kidneys, respectively. Finally, physiological relevance of siRNA SORT LNP-mediated gene silencing is established via acute suppression of endogenous Tie2 which induces lung-specific phenotypic alteration of vascular endothelial barrier. Due to plethora of extrahepatic diseases that may benefit from RNAi interventions, it is anticipated that the findings will expand preclinical landscape of therapeutic targets beyond the liver.
Keywords: Selective ORgan Targeting (SORT); extrahepatic siRNA silencing; kidney siRNA delivery; lipid nanoparticles (LNPs); unbiased knockdown.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures

References
-
- Mendes BB, Conniot J, Avital A, Yao D, Jiang X, Zhou X, Sharf-Pauker N, Xiao Y, Adir O, Liang H, Shi J, Schroeder A, Conde J, Nat Rev Methods Primers 2022, 2; - PMC - PubMed
- Yonezawa S, Koide H, Asai T, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2020, 154–155, 64; - PMC - PubMed
- Akinc A, Maier MA, Manoharan M, Fitzgerald K, Jayaraman M, Barros S, Ansell S, Du X, Hope MJ, Madden TD, Mui BL, Semple SC, Tam YK, Ciufolini M, Witzigmann D, Kulkarni JA, van der Meel R, Cullis PR, Nat Nanotechnol 2019, 14, 1084; - PubMed
- d)Narasipura EA, VanKeulen-Miller R, Ma Y, Fenton OS, Bioconjug Chem 2023, 34, 1177; - PubMed
- Setten RL, Rossi JJ, Han SP, Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020, 19, 291; - PubMed
- Kulkarni JA, Witzigmann D, Chen S, Cullis PR, van der Meel R, Acc Chem Res 2019, 52, 2435. - PubMed
-
- Gomes-da-Silva LC, Fonseca NA, Moura V, Pedroso de Lima MC, Simoes S, Moreira JN, Acc Chem Res 2012, 45, 1163. - PubMed
-
- Lorenzer C, Dirin M, Winkler AM, Baumann V, Winkler J, J Control Release 2015, 203, 1; - PubMed
- Dong Y, Siegwart DJ, Anderson DG, Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2019, 144, 133; - PMC - PubMed
- Brown KM, Nair JK, Janas MM, Anglero-Rodriguez YI, Dang LTH, Peng H, Theile CS, Castellanos-Rizaldos E, Brown C, Foster D, Kurz J, Allen J, Maganti R, Li J, Matsuda S, Stricos M, Chickering T, Jung M, Wassarman K, Rollins J, Woods L, Kelin A, Guenther DC, Mobley MW, Petrulis J, McDougall R, Racie T, Bombardier J, Cha D, Agarwal S, Johnson L, Jiang Y, Lentini S, Gilbert J, Nguyen T, Chigas S, LeBlanc S, Poreci U, Kasper A, Rogers AB, Chong S, Davis W, Sutherland JE, Castoreno A, Milstein S, Schlegel MK, Zlatev I, Charisse K, Keating M, Manoharan M, Fitzgerald K, Wu JT, Maier MA, Jadhav V, Nat Biotechnol 2022, 40, 1500. - PubMed
-
- Dilliard SA, Siegwart DJ, Nat Rev Mater 2023, 8, 282; - PMC - PubMed
- Paunovska K, Loughrey D, Dahlman JE, Nat Rev Genet 2022, 23, 265; - PMC - PubMed
- Kanasty R, Dorkin JR, Vegas A, Anderson D, Nat Mater 2013, 12, 967; - PubMed
- Akinc A, Zumbuehl A, Goldberg M, Leshchiner ES, Busini V, Hossain N, Bacallado SA, Nguyen DN, Fuller J, Alvarez R, Borodovsky A, Borland T, Constien R, de Fougerolles A, Dorkin JR, Narayanannair Jayaprakash K, Jayaraman M, John M, Koteliansky V, Manoharan M, Nechev L, Qin J, Racie T, Raitcheva D, Rajeev KG, Sah DW, Soutschek J, Toudjarska I, Vornlocher HP, Zimmermann TS, Langer R, Anderson DG, Nat Biotechnol 2008, 26, 561. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA269787-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 5R01EB025192-06/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA269787/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I-2123-20220031/Welch Foundation
- UTSW Metabolic Phenotyping Core
- P30 CA142543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Moody Foundation Flow Cytometry Facility
- P30CA142543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- SIEGWA18XX0/Cystic Fibrosis Foundation
- RP220582/Cryo-Electron Microscopy Facility
- R01 EB025192/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas
- SIEGWA21XX0/Cystic Fibrosis Foundation
- UTSW Proteomics Core
- RP170644/Cryo-Electron Microscopy Facility
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UTSW Tissue Management Shared Resource
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

