Diagnostic performance of the O-RADS MRI system for magnetic resonance imaging in discriminating benign and malignant adnexal lesions: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
- PMID: 38973658
- PMCID: PMC12057528
- DOI: 10.4274/dir.2024.242784
Diagnostic performance of the O-RADS MRI system for magnetic resonance imaging in discriminating benign and malignant adnexal lesions: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Abstract
Purpose: After the introduction of the Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System (O-RADS) for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), several studies with diverse characteristics have been published to assess its diagnostic performance. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the diagnostic performance of O-RADS MRI scoring for adnexal masses, accounting for the risk of selection bias.
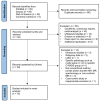
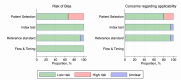
Methods: The PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases were searched for eligible studies. Borderline or malignant lesions were considered malignant. All O-RADS MRI scores ≥4 were considered positive. The quality of the studies was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratio (LR) values were calculated, considering the risk of selection bias.
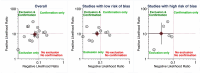
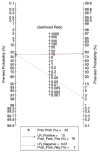
Results: Fifteen eligible studies were found, and five of them had a high risk of selection bias. Between-study heterogeneity was low-to-moderate for sensitivity but substantial for specificity (I2 values were 35.5% and 64.7%, respectively). The pooled sensitivity was significantly lower in the studies with a low risk of bias compared with those with a high risk of bias (93.0% and 97.5%, respectively; P = 0.043), whereas the pooled specificity was not different (90.4% for the overall population). The negative and positive LRs were 0.08 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.05–0.11] and 10.0 (95% CI 7.7–12.9), respectively, for the studies with low risk of bias and 0.03 (95% CI 0.01–0.10) and 10.3 (95% CI 3.8–28.3), respectively, for those with high risk of bias.
Conclusion: The overall diagnostic performance of the O-RADS system is very high, particularly for ruling out borderline/malignant lesions, but with a moderate ruling-in potential. Studies with a high risk of selection bias lead to an overestimation of sensitivity.
Clinical significance: The O-RADS system demonstrates considerable diagnostic performance, particularly in ruling out borderline or malignant lesions, and should routinely be used in practice. The high between-study heterogeneity observed for specificity suggests the need for improvement in the consistent characterization of the benign lesions to reduce false positive rates.
Keywords: Adnexal mass; ovarian cancer; Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System; agnetic resonance imaging; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Copyright© Author(s) - Available online at dirjournal.org. Content of this journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure: The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Value of MRI-Based Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System for the Diagnosis of Adnexal Masses.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024 Dec;46(6):909-917. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.16176. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39773510
-
Ovarian Adnexal Reporting Data System (O-RADS) for Classifying Adnexal Masses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;14(13):3151. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133151. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Ultrasonography-Based Risk Models in Differentiating Between Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors in a US Cohort.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2323289. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.23289. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37440228 Free PMC article.
-
O-RADS MRI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Performance and Category-wise Malignancy Rates.Radiology. 2023 Apr;307(1):e220795. doi: 10.1148/radiol.220795. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 36413127
-
Diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) combined with Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System (O-RADS) ultrasound risk stratification for adnexal masses: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Radiol. 2024 Sep;79(9):e1167-e1175. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2024.05.021. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Clin Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38942707
Cited by
-
Efficacy of a combination of O-RADS, CEUS, and CA125, in identification of ovary-adnexal malignant lesions.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 15;15(2):631-642. doi: 10.62347/JHJJ1149. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40084369 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data System Magnetic Resonance Imaging (O-RADS MRI): A Review of Its Evolution, Current Advances, and Persistent Challenges in Ovarian Imaging.Cureus. 2025 Jun 25;17(6):e86717. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86717. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40718198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reinhold C, Rockall A, Sadowski EA, et al. Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting Lexicon for MRI: A White Paper of the ACR Ovarian-Adnexal Reporting and Data Systems MRI Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18(5):713–729. - PubMed
-
- Bang JI, Kim JY, Choi MC, Lee HY, Jang SJ. Application of multimodal imaging biomarker in the differential diagnosis of ovarian mass: integration of conventional and molecular imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2022;47(2):117–122. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Pame M, Bhuyan R, Roy DK, James VM. Diagnostic Performance of O-RADS MRI scoring system for the assessment of adnexal masses in routine clinical radiology practice- a single tertiary centre prospective cohort study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2022;16(4):TC11–TC16.
-
- Campos A, Villermain-Lécolier C, Sadowski EA, et al. O-RADS scoring system for adnexal lesions: diagnostic performance on TVUS performed by an expert sonographer and MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2023;169:111172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

