Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Phosphoserine Phosphatase: A Novel Target for the Development of Antiamoebic Drugs
- PMID: 38973836
- PMCID: PMC11223228
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09439
Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Phosphoserine Phosphatase: A Novel Target for the Development of Antiamoebic Drugs
Abstract
Amoebiasis, a widespread disease caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica, poses challenges due to the adverse effects of existing antiamoebic drugs and rising drug resistance. Novel targeted drugs are in need of the hour to combat the prevalence of this disease. Given the significance of cysteine for Entamoeba survival, the rate-determining step in the serine (the sole substrate of cysteine synthesis) biosynthetic pathway, i.e., the conversion of 3-phosphoserine to l-serine catalyzed by phosphoserine phosphatase (PSP), emerges as a promising drug target. Our previous study unveils the essential role of EhPSP in amoebas' survival, particularly under oxidative stress, by increasing cysteine production. The study also revealed that EhPSP differs significantly from its human counterpart, both structurally and biochemically, highlighting its potential as a viable target for developing new antiamoebic drugs. In the present study, employing in silico screening of vast natural and synthetic small chemical compound libraries, we identified 21 potential EhPSP inhibitor molecules. Out of the 21 compounds examined, only five could inhibit the catalytic activity of EhPSP. The inhibition capability of these five compounds was subsequently validated by in silico binding free energy calculations, SPR-based real-time binding studies, and molecular simulations to assess the stability of the EhPSP-inhibitor complexes. By identifying the five potential inhibitors that can target cysteine synthesis via EhPSP, our findings establish EhPSP as a drug candidate that can serve as a foundation for antiamoebic drug research.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





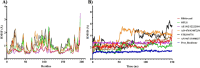
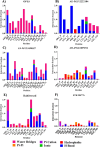
References
-
- Ehrenkaufer G. M.; Suresh S.; Solow-Cordero D.; Singh U. High-Throughput Screening of Entamoeba Identifies Compounds Which Target Both Life Cycle Stages and Which Are Effective Against Metronidazole Resistant Parasites. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 276. 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00276. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
