Geochemistry of Pelites at Chengmen Area: Implications for Sediments Resource and Tectonic Environment
- PMID: 38973845
- PMCID: PMC11223246
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00597
Geochemistry of Pelites at Chengmen Area: Implications for Sediments Resource and Tectonic Environment
Abstract
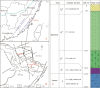
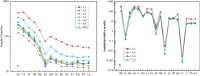
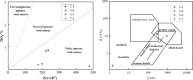
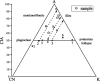
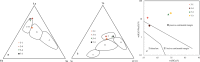
The pelite samples were collected from drillholes from the Chengmen area of the Fuzhou Basin of Fujian, China to reveal the sediments resource and tectonic environment of these pelites via an analysis of its lithology and geochemistry. The rare earth element distribution pattern of the pelites exhibited a high degree of fractionation between light and heavy rare earth elements, moderate negative Eu anomalies, and positive Ce anomalies, which are consistent with the rare earth element distribution pattern of Minjiang sediments and Fujian soils. Moreover, the variations in trace elements are also generally consistent, indicating a common provenance. The extremely high chemical index of alteration (CIA) and index of chemical variability (ICV) values of the pelites suggest that the source area experienced intense weathering, indicating a subtropical hot and humid climate environment in the source area and the Fuzhou Basin at that time. The source rock attribute discrimination diagrams show that the main source of pelites is felsic igneous rocks. The ratios of REDOX parameters show that during the sedimentary period, the water body in the study area was predominantly in an oxidizing environment. Furthermore, the tectonic background diagrams reveal that the source area underwent geological tectonic evolution processes of active and passive continental margins, marking the transition from the continental margin above the subduction of the ancient Pacific plate to the continental margin extension after subduction cessation.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatia M. R.; Crook K. A. W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1986, 92 (2), 181–193. 10.1007/BF00375292. - DOI
-
- McLennan S. M.; Hemming S.; McDaniel D. K.; Hanson G. N.; Johnsson M. J.; Basu A.. Geochemical Approaches to Sedimentation, Provenance, and Tectonics. In Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments; Geological Society of America, 1993; Vol. 284, p 21.
-
- Rimmer S. M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian–Mississippian black shales, Central Appalachian Basin (USA). Chem. Geol. 2004, 206 (3–4), 373–391. 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.029. - DOI
-
- Tribovillard N.; Algeo T. J.; Lyons T.; Riboulleau A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232 (1–2), 12–32. 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012. - DOI
-
- Yang S.; Yim W. W. S.; Huang G. Geochemical composition of inner shelf Quaternary sediments in the northern South China Sea with implications for provenance discrimination and paleoenvironmental reconstruction. Global Planet. Change 2008, 60 (3), 207–221. 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.02.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
