An Efficient p-n Heterojunction Copper Tin Sulfide/g-C3N4 Nanocomposite for Methyl Orange Photodegradation
- PMID: 38973891
- PMCID: PMC11223204
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02414
An Efficient p-n Heterojunction Copper Tin Sulfide/g-C3N4 Nanocomposite for Methyl Orange Photodegradation
Abstract
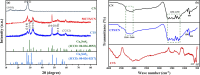
The discharge of toxic dye effluents from industry is a major concern for environmental pollution and toxicity. These toxic dyes can be efficiently removed from waste streams using a photocatalysis process involving visible light. Due to its simple synthesis procedure, inexpensive precursor, and robust stability, graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4, or CN) has been used as a visible light responsive catalyst for the degradation of dyes with mediocre performance because it is limited by its low visible light harvesting capability due to its wide bandgap and fast carrier recombination rate. To overcome these limitations and enhance the performance of g-C3N4, it was coupled with a narrow bandgap copper tin sulfide (CTS) semiconductor to form a p-n heterojunction. CTS and g-C3N4 were selected due to their good stability, low toxicity, ease of synthesis, layered sheet/plate-like morphology, and relatively abundant precursors. Accordingly, a series of copper tin sulfide/graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites (CTS/g-C3N4) with varying CTS contents were successfully synthesized via a simple two-step process involving thermal pyrolysis and coprecipitation for visible-light-induced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (MO) dye. The photocatalytic activity results showed that the 50%(wt/wt) CTS/g-C3N4 composite displayed a remarkable degradation efficiency of 95.6% for MO dye under visible light illumination for 120 min, which is higher than that of either pristine CTS or g-C3N4. The improved performance is attributed to the extended light absorption range (due to the optimized bandgap), effective suppression of photoinduced electron-hole recombination, and improved charge transfer that arose from the formation of a p-n heterojunction, as evidenced by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), photocurrent, and photoluminescence results. Moreover, the results of the reusability study showed that the composite has excellent stability, indicating its potential for the degradation of MO and other toxic organic dyes from waste streams.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Facile fabrication of novel porous graphitic carbon nitride/copper sulfide nanocomposites with enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic performance.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Aug 15;476:132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.05.024. Epub 2016 May 14. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 27209398
-
Fabrication and efficient visible light photocatalytic properties of novel zinc indium sulfide (ZnIn2S4) - graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)/bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) nanorod-based ternary nanocomposites with enhanced charge separation via Z-scheme transfer.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Nov 15;482:58-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.062. Epub 2016 Jul 26. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 27491002
-
Copper iodide decorated graphitic carbon nitride sheets with enhanced visible-light response for photocatalytic organic pollutant removal and antibacterial activities.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Jan 15;208:111712. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111712. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33396043
-
Graphitic carbon nitride based nanocomposites for the photocatalysis of organic contaminants under visible irradiation: Progress, limitations and future directions.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Aug 15;633:546-559. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.206. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29579666 Review.
-
g-C3N4 Based Photocatalyst for the Efficient Photodegradation of Toxic Methyl Orange Dye: Recent Modifications and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2023 Apr 4;28(7):3199. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073199. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abass A. K.; Raoof S. D. Advanced Oxidation Process Treatment for Azo Dyes Pollutants Using Ultra-Violet Irradiation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1664, 01206610.1088/1742-6596/1664/1/012066. - DOI
-
- Sen S. K.; Raut S.; Bandyopadhyay P.; Raut S. Fungal Decolouration and Degradation of Azo Dyes: A Review. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2016, 30 (3), 112–133. 10.1016/j.fbr.2016.06.003. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya P.; Swarnakar S.; Ghosh S.; Majumdar S.; Banerjee S. Disinfection of Drinking Water via Algae Mediated Green Synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Toxicity Evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7 (1), 10286710.1016/j.jece.2018.102867. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
