pH-Sensitive Hydrogels Fabricated with Hyaluronic Acid as a Polymer for Site-Specific Delivery of Mesalamine
- PMID: 38973903
- PMCID: PMC11223520
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03240
pH-Sensitive Hydrogels Fabricated with Hyaluronic Acid as a Polymer for Site-Specific Delivery of Mesalamine
Abstract
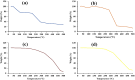
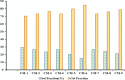
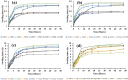
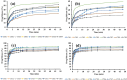
Hydrogels with the main objective of releasing mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid) in the colon in a modified manner were formulated in the present work using a free-radical polymerization approach. Different ratios of hyaluronic acid were cross-linked with methacrylic and acrylic acids using methylenebis(acrylamide). The development of a new polymeric network and the successful loading of drug were revealed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Thermogravimetric analysis demonstrated that the hydrogel was more thermally stable than the pure polymer and drug. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed a rough and hard surface which was relatively suitable for efficient loading of drug and significant penetration of dissolution medium inside the polymeric system. Studies on swelling and drug release were conducted at 37 °C in acidic and basic conditions (pH 1.2, 4.5, 6.8, and 7.4, respectively). Significant swelling and drug release occurred at pH 7.4. Swelling, drug loading, drug release, and gel fraction of the hydrogels increased with increasing hyaluronic acid, methacrylic acid, and acrylic acid concentrations, while the sol fraction decreased. Results obtained from the toxicity study proved the formulated system to be safe for biological systems. The pH-sensitive hydrogels have the potential to be beneficial for colon targeting due to their pH sensitivity and biodegradability. Inflammatory bowel disease may respond better to hydrogel treatment as compared to conventional dosage forms. Specific amount of drug is released from hydrogels at specific intervals to maintain its therapeutic concentration at the required level.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cevallos S. A.; Lee J. Y.; Velazquez E. M.; Foegeding N. J.; Shelton C. D.; Tiffany C. R.; Parry B. H.; Stull-Lane A. R.; Olsan E. E.; Savage H. P.; et al. 5-Aminosalicylic acid ameliorates colitis and checks dysbiotic Escherichia coli expansion by activating PPAR-γ signaling in the intestinal epithelium. Mbio 2021, 12 (1), e03227-20 10.1128/mbio.03227-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
