Lactobacillus rhamnosus 069 and Lactobacillus brevis 031: Unraveling Strain-Specific Pathways for Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Attenuating High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice
- PMID: 38973907
- PMCID: PMC11223209
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02514
Lactobacillus rhamnosus 069 and Lactobacillus brevis 031: Unraveling Strain-Specific Pathways for Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Attenuating High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice
Abstract
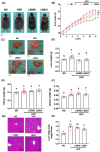
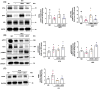
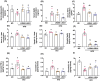
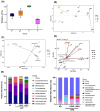
Obesity is a global health crisis, marked by excessive fat in tissues that function as immune organs, linked to microbiota dysregulation and adipose inflammation. Investigating the effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus SG069 (LR069) and Lactobacillus brevis SG031 (LB031) on obesity and lipid metabolism, this research highlights adipose tissue's critical immune-metabolic role and the probiotics' potential against diet-induced obesity. Mice fed a high-fat diet were treated with either LR069 or LB031 for 12 weeks. Administration of LB031 boosted lipid metabolism, indicated by higher AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) phosphorylation, and increased the M2/M1 macrophage ratio, indicating LB031's anti-inflammatory effect. Meanwhile, LR069 administration not only led to significant weight loss by enhancing lipolysis which evidenced by increased phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) but also elevated Akkermansia and fecal acetic acid levels, showing the gut microbiota's pivotal role in its antiobesity effects. LR069 and LB031 exhibit distinct effects on lipid metabolism and obesity, underscoring their potential for precise interventions. This research elucidates the unique impacts of these strains on metabolic health and highlights the intricate relationship between gut microbiota and obesity, advancing our knowledge of probiotics' therapeutic potential.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tiwari A.; Balasundaram P.; Public Health Considerations Regarding Obesity; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, 2023. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
