An Empirical Investigation of the Relationships Among Self-Esteem, Depression and Self-Serving Bias in People with Internet Gaming Disorder
- PMID: 38973976
- PMCID: PMC11227327
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S462184
An Empirical Investigation of the Relationships Among Self-Esteem, Depression and Self-Serving Bias in People with Internet Gaming Disorder
Abstract
Introduction: People are generally characterized by a self-serving bias which describes the tendency to ascribe positive outcomes or success to internal or personal causes (self-enhancement motivation) and ascribe negative outcomes or failure to external or situational causes (self-protection motivation). It has been found that the individuals with internet gaming disorder (IGD) who have low self-esteem and high depression exhibit an attenuated self-serving bias. However, the relationships among self-esteem, depression and self-serving bias are not clearly identified.
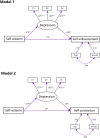
Methods: A sample of 138 IGD participants completed self-esteem and depression scales and a causal attribution task (Study 1) to examine the relationships among self-esteem, depression and self-serving bias (both self-enhancement and self-protection). In follow-up Study 2, 28 IGD participants were recruited to undertake self-affirmation intervention which can affirm one's sense of global self-view and bolster self-esteem to explore whether self-affirmation would trigger a reduction of depression and a raise of self-serving bias.
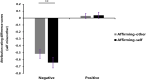
Results: The results of path analysis in Study 1 showed that the self-serving bias was predicted by self-esteem and depression, and the depression played a mediating role between self-esteem and self-serving bias. The results of Study 2 showed that the IGD participants reported higher self-esteem, lower depression and engaged in more self-protection motivation after affirming-self manipulation as compared with affirming-other manipulation.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that self-esteem predicts self-serving bias through depression and self-affirmation could trigger an increase of self-esteem, further decrease depression and improve self-serving bias for the individuals with IGD. The present article clearly identified the relationships among these factors and provided a new approach to promote positive self-concept in individuals with IGD. Future research is warranted to explore the lasting benefits of self-affirmation on domains of education, relationships and gaming withdrawal for the individuals with IGD among different populations.
Keywords: depression; internet gaming disorder; self-esteem; self-serving bias.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Yifan Wang and Lei Zhang are co-first authors for this study. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests with regard to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Internet Gaming Addiction: a Systematic Review of Empirical Research. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2012;10(2):278–296. doi: 10.1007/s11469-011-9318-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

