PGM5-AS1 Promotes Progression of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Immune Escape by Regulating miR-503-5p
- PMID: 38973995
- PMCID: PMC11225957
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S453245
PGM5-AS1 Promotes Progression of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Immune Escape by Regulating miR-503-5p
Abstract
Purpose: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a prevalent malignant condition with a dismal prognosis. LncRNA PGM5 antisense RNA 1 (PGM5-AS1) appears to be intricately involved in the progression of DLBCL, yet the modulatory mechanism remains unclear. The purpose of this study was to explore the expression of lncRNA PGM5-AS1 in DLBCL and its effect on the disease progression of DLBCL, as well as to explore its mechanisms.
Patients and methods: A total of 35 patients were included in the study. The expression levels of PGM5-AS1 and miR-503-5p in DLBCL tumor tissues and cell lines were detected by RT-qPCR. Cell proliferation was assessed using CCK8. Apoptosis rate was determined by flow cytometry. Cell invasion was examined by transwell assays. The specific interaction between PGM5-AS1 and miR-503-5p was verified through dual luciferase reporter gene assays. The immune related factors were detected by ELASA kits. The CD8+ T cells cytotoxicity was evaluated by LDH cytotoxicity kit.
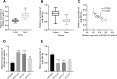
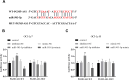
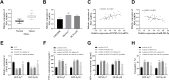
Results: In DLBCL tumor tissues and cells, upregulated PGM5-AS1 expression, downregulated miR-503-5p expression, and elevated PD-L1 expression were observed. PGM5-AS1 functioned as a regulator in controlling DLBCL cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion by downregulating miR-503-5p expression. When CD8+ T cells were co-cultured with cells transfected with si-PGM5-AS1, the secretion of immunoregulatory factors increased, and the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells increased. These effects were mitigated by miR-503-5p inhibitors.
Conclusion: PGM5-AS1 accelerated DLBCL development and facilitated tumor immune escape through the miR-503-5p. Our discoveries offered an insight into lncRNA PGM5-AS1 serving as a prospective therapeutic target for DLBCL.
Keywords: DLBCL; PGM5-AS1; immune escape; miR-503-5p.
© 2024 Qin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LncRNA PGM5-AS1 inhibits the progression of breast cancer by inhibiting miR-182-5p.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2025 Apr 29:1-14. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2025.2498642. Online ahead of print. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40298102
-
Reduced long noncoding RNA PGM5-AS1 facilitated proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer through sponging miR-100-5p.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Aug;24(15):7972-7981. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202008_22480. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32767323
-
LncRNA PGM5-AS1 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting miRNA-423-5p/SLIT2 axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jun 20;24(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03402-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38902704 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by impairing miR-140-5p-mediated FBN1 inhibition.Mol Oncol. 2020 Oct;14(10):2660-2677. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12711. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Mol Oncol. 2020. Retraction in: Mol Oncol. 2023 Aug;17(8):1692. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13482. PMID: 32412676 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Silencing of OIP5-AS1 Protects Endothelial Cells From ox-LDL-Triggered Injury by Regulating KLF5 Expression via Sponging miR-135a-5p.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 12;8:596506. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.596506. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33778018 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LncRNA PGM5-AS1 Impairs the Resistance of Cervical Cancer to Cisplatin by Regulating the Hippo and PI3K-AKT Pathways.Biochem Genet. 2024 Dec 28. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-11011-0. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39733221
-
FOXM1 upregulation, promotes immune escape in gastric cancer through activation of Notch signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 11. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05322-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40498401
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

