Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between the Fixed-Dose Combination of Ezetimibe/Rosuvastatin 10/20 Mg and the Fixed-Dose Combination of Telmisartan/Amlodipine 80/5 Mg in Healthy Subjects
- PMID: 38974125
- PMCID: PMC11225994
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S465652
Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between the Fixed-Dose Combination of Ezetimibe/Rosuvastatin 10/20 Mg and the Fixed-Dose Combination of Telmisartan/Amlodipine 80/5 Mg in Healthy Subjects
Abstract
Background: Management of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, which are common comorbid risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, require multiple medications. The development of a fixed-dose combination (FDC) containing ezetimibe, rosuvastatin, telmisartan, and amlodipine aims to enhance patient adherence and persistence, but the potential interactions among the four medications have not been studied. This study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetic (PK) interactions between the FDC of ezetimibe/rosuvastatin 10/20 mg (ER) and the FDC of telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg (TA).
Methods: An open-label, single-sequence, three-period, three-treatment crossover study was conducted in healthy male subjects. All subjects received ER for 7 days, TA for 9 days and ER combined with TA for 7 days during each treatment period. For PK analysis of total/free ezetimibe, rosuvastatin, telmisartan, and amlodipine, serial blood samples were collected for 24 hours at steady state. Safety profiles were assessed throughout the study.
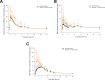
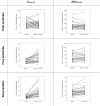
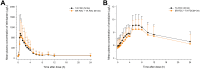
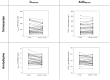
Results: Thirty-eight subjects were enrolled, and 34 subjects completed the study. The systemic exposure to each active ingredient after coadministration of the two FDCs was similar to that after each FDC alone. The geometric mean ratios and 90% confidence intervals for the maximum plasma concentration (µg/L) and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (h·µg/L) of the combination therapy to monotherapy, assessed at steady state, were as follows: total ezetimibe, 1.0264 (0.8765-1.2017) and 0.9359 (0.7847-1.1163); free ezetimibe, 1.5713 (1.2821-1.9257) and 0.9941 (0.8384-1.1788); rosuvastatin, 2.1673 (1.7807-2.6379) and 1.1714 (0.9992-1.3733); telmisartan, 1.0745 (0.8139-1.4186) and 1.1057 (0.8379-1.4591); and amlodipine, 0.9421 (0.8764-1.0126) and 0.9603 (0.8862-1.0405). Both combination therapy and monotherapy were well tolerated by the subjects.
Conclusion: The coadministration of ezetimibe/rosuvastatin 10/20 mg and ezetimibe/rosuvastatin 10/20 mg was well tolerated in healthy subjects, and the PK interaction between those two FDCs was not clinically significant.
Keywords: amlodipine; drug‒drug interactions; ezetimibe; fixed-dose combination; pharmacokinetics; rosuvastatin; telmisartan.
© 2024 Ryu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Kyung Tae Kim is a full-time employee of Addpharma. The other authors report no conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

