Longitudinal evaluation of laboratory results and method precision in worldwide erythropoietin external quality assessments
- PMID: 38974321
- PMCID: PMC11224661
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1390079
Longitudinal evaluation of laboratory results and method precision in worldwide erythropoietin external quality assessments
Abstract
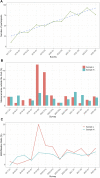
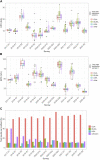
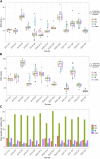
Introduction: This study presents a longitudinal analysis of external quality assessment (EQA) results for erythropoietin (EPO) determinations conducted between 2017 and 2022 with a continuously increasing number of participating laboratories. The aim of this work was to evaluate participant performance and methodological aspects. Methods: In each of the eleven EQA surveys, a blinded sample set of lyophilized human serum containing one sample with lower EPO concentrations (L) and one with higher EPO concentrations (H) was sent to the participating laboratories. Results: A total of 1,256 measurements were included. The median (interquartile range) fraction of participants not meeting the criteria of acceptance set at 20% around the robust mean of the respective survey was 9.5% (6.1%-10.7%) (sample L) and 9.1% (5.8%-11.8%) (sample H) but lacked a clear trend in the observed period. Some surveys exhibited unusually high interlaboratory variation, suggesting interfering components in the EQA samples. Different immunological methods and reagent manufacturers also showed variability in measurement outcomes to some extent. Conclusion: These findings highlight the need for continuous quality assessment in EPO measurements to ensure patient safety and identify areas for further research and investigation.
Keywords: erythropoietin; external quality assessment; immunoassay; method precision; proficiency testing.
Copyright © 2024 Toll, Weiss, Vierbaum, Schellenberg, Thevis and Wenzel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A sample distribution programme for erythropoietin.Clin Lab Haematol. 2006 Aug;28(4):228-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.2006.00786.x. Clin Lab Haematol. 2006. PMID: 16898959
-
External quality assurance program for diagnostic complement laboratories: evaluation of the results of the past seven years.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1368399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1368399. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596685 Free PMC article.
-
A 3-year-long investigation of the authenticity of the return results of hepatitis B virus qualitative testing in external quality assessment in East China.J Med Virol. 2019 Jun;91(6):1076-1080. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25431. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 30761566
-
External quality assessment of hormone determinations.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec;27(6):803-22. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24275192 Review.
-
The CNR external quality assessment program for immunoassays: statistical analysis and reports for participants.Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1991;27(3):469-77. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1991. PMID: 1809067 Review.
References
-
- Abellan R., Ventura R., Pichini S., Remacha A. F., Pascual J. A., Pacifici R., et al. (2004). Evaluation of immunoassays for the measurement of erythropoietin (EPO) as an indirect biomarker of recombinant human EPO misuse in sport. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 35, 1169–1177. 10.1016/j.jpba.2004.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alhajj M., Farhana A. (2022). “Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,” in StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; ). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555922/(Accessed March 8, 2022). - PubMed
-
- Beckman Coulter, Inc (2020). “ACCESS immunoassay systems, instructions for use,” in Access EPO calibrators erythropoietin, REF A16365. Available at: https://www.beckmancoulter.com/download/file/phxB50133J-EN_US/B50133J?ty... (Accessed January 30, 2024).
-
- Beckman Coulter, Inc (2023). Beckman coulter ACCESS immunoassay systems. Access EPO Erythropoietin - Instr. Use. Available at: https://www.beckmancoulter.com/download/file/phxC94197A-EN_US/C94197A?ty... (Accessed January 30, 2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

