Effect of post-harvest drying period on the chemical composition of Zingiber zerumbet Sm. Rhizomes essential oil and its biological activities
- PMID: 38974360
- PMCID: PMC11222349
- DOI: 10.1007/s12298-024-01468-z
Effect of post-harvest drying period on the chemical composition of Zingiber zerumbet Sm. Rhizomes essential oil and its biological activities
Abstract
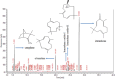
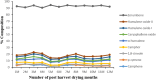
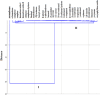
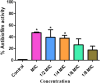
Zingiber zerumbet Sm. (Family: Zingiberaceae) is an important perennial medicinal oil-bearing herb that is native to the Southeast Asia. This study examines the impact of different durations of post-harvest shade drying (ranging from 1 to 12 months) on essential oil yield and chemical composition of Z. zerumbet, in comparison to the freshly collected oil sample. This study explores how post-harvest shade drying impact the composition and longevity of Z. zerumbet rhizomes as well as its antimicrobial, antibiofilm activity. The oils were analyzed for their chemical composition analysis using a gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The post-harvest periods of drying (1-12 months) were discovered to enhance the concentration of marker constituents in the oil. The primary constituent, Zerumbone, was detected in concentrations ranging from 69.38 ± 5.63% to a maximum of 80.19 ± 1.53% as the drying duration of the rhizome was extended. The output of the essential oil was not significantly affected by drying times; however, it did have a noticeable impact on the proportions of monoterpenes. Both disc diffusion and broth microdilution assay were used in freshly collected Z. zerumbet oil for its antimicrobial potential against S. aureus, L. monocytogens, S. hominis, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, P. aeruginosa, S. intermedius, E. coli, and C. albicans. For the first time, the oil reported to exhibit antibiofilm activity against S. aureus which was validated using fluorescence microscopy, and effectively disrupts the biofilm by 47.38% revealing that essential oil was able to disintegrate the clusters of the pathogen. Z. zerumbet rhizome oil is effective to reduce food-borne microorganisms. Therefore, its essential oil, a natural source of bioactive zerumbone, may improve flavor, aroma, and preservation.
Keywords: Antibiofilm activity; Fluorescence microscopy; Post-harvest shade-drying; Zerumbone; Zingiber zerumbet.
© Prof. H.S. Srivastava Foundation for Science and Society 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Standardized ethanol extract, essential oil and zerumbone of Zingiber zerumbet rhizome suppress phagocytic activity of human neutrophils.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2748-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31752812 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Chemical Composition and Bioactivities of Essential Oils from Fresh and Dry Rhizomes of Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Smith.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 11;2020:9641284. doi: 10.1155/2020/9641284. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32104711 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition of the essential oil of Zingiber zerumbet var. darcyi.Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Oct;7(10):1369-70. Nat Prod Commun. 2012. PMID: 23157013
-
Major Bioactive Compounds in Essential Oils Extracted From the Rhizomes of Zingiber zerumbet (L) Smith: A Mini-Review on the Anti-allergic and Immunomodulatory Properties.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 20;9:652. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00652. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29973880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Roscoe ex Sm.: biotechnological advancements and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;107(18):5613-5625. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12682-2. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37480373 Review.
References
-
- Adams RP. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Carol Stream: Allured Publishing Corporation; 2007.
-
- Aji N, Kumala S, Mumpuni E, Rahmat D. Antibacterial activity and active fraction of zingiber officinale roscoe, Zingiber montanum (J.Koenig) Link ex A, and Zingiber zerumbet (L) Roscoe ex Sm. against propionibacterium acnes. Pharmacogn J. 2022;14(1):103–111.
-
- Bhavaniramya S, Vishnupriya S, Al-Aboody MS, Vijayakumar R, Baskaran D. Role of essential oils in food safety: antimicrobial and antioxidant applications. GOST. 2019;2:49–55.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
