Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and shear-wave elastography for small breast nodules
- PMID: 38974410
- PMCID: PMC11227273
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17677
Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and shear-wave elastography for small breast nodules
Abstract
Background: The study aims to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and shear-wave elastography (SWE) in detecting small malignant breast nodules in an effort to inform further refinements of the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) classification system.
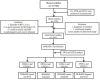
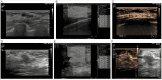
Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed patients with breast nodules who underwent conventional ultrasound, CEUS, and SWE at Gongli Hospital from November 2015 to December 2019. The inclusion criteria were nodules ≤ 2 cm in diameter with pathological outcomes determined by biopsy, no prior treatments, and solid or predominantly solid nodules. The exclusion criteria included pregnancy or lactation and low-quality images. Imaging features were detailed and classified per BI-RADS. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curves.
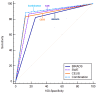
Results: The study included 302 patients with 305 breast nodules, 113 of which were malignant. The diagnostic accuracy was significantly improved by combining the BI-RADS classification with CEUS and SWE. The combined approach yielded a sensitivity of 88.5%, specificity of 87.0%, positive predictive value of 80.0%, negative predictive value of 92.8%, and accuracy of 87.5% with an area under the curve of 0.877. Notably, 55.8% of BI-RADS 4A nodules were downgraded to BI-RADS 3 and confirmed as benign after pathological examination, suggesting the potential to avoid unnecessary biopsies.
Conclusion: The integrated use of the BI-RADS classification, CEUS, and SWE enhances the accuracy of differentiating benign and malignant small breast nodule, potentially reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies.
Keywords: BI-RADS classification; Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; Shear-wave elastography; Small breast nodule; Ultrasound.
©2024 Shen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aouad P, Saikali M, Abdel-Samad R, Fostok S, El-Houjeiri L, Pisano C, Talhouk R, Darwiche N. Antitumor activities of the synthetic retinoid ST1926 in two-dimensional and three-dimensional human breast cancer models. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2017;28:757–770. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000511. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonsu AB, Ncama BP. Evidence of promoting prevention and the early detection of breast cancer among women, a hospital-based education and screening interventions in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review protocol. Systematic Reviews. 2018;7:234. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0889-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

