HaMADS3, HaMADS7, and HaMADS8 are involved in petal prolongation and floret symmetry establishment in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
- PMID: 38974413
- PMCID: PMC11225715
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17586
HaMADS3, HaMADS7, and HaMADS8 are involved in petal prolongation and floret symmetry establishment in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
Abstract
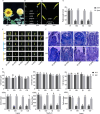
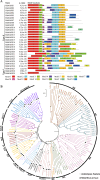
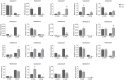
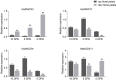
The development of floral organs, crucial for the establishment of floral symmetry and morphology in higher plants, is regulated by MADS-box genes. In sunflower, the capitulum is comprised of ray and disc florets with various floral organs. In the sunflower long petal mutant (lpm), the abnormal disc (ray-like) floret possesses prolongated petals and degenerated stamens, resulting in a transformation from zygomorphic to actinomorphic symmetry. In this study, we investigated the effect of MADS-box genes on floral organs, particularly on petals, using WT and lpm plants as materials. Based on our RNA-seq data, 29 MADS-box candidate genes were identified, and their roles on floral organ development, especially in petals, were explored, by analyzing the expression levels in various tissues in WT and lpm plants through RNA-sequencing and qPCR. The results suggested that HaMADS3, HaMADS7, and HaMADS8 could regulate petal development in sunflower. High levels of HaMADS3 that relieved the inhibition of cell proliferation, together with low levels of HaMADS7 and HaMADS8, promoted petal prolongation and maintained the morphology of ray florets. In contrast, low levels of HaMADS3 and high levels of HaMADS7 and HaMADS8 repressed petal extension and maintained the morphology of disc florets. Their coordination may contribute to the differentiation of disc and ray florets in sunflower and maintain the balance between attracting pollinators and producing offspring. Meanwhile, Pearson correlation analysis between petal length and expression levels of MADS-box genes further indicated their involvement in petal prolongation. Additionally, the analysis of cis-acting elements indicated that these three MADS-box genes may regulate petal development and floral symmetry establishment by regulating the expression activity of HaCYC2c. Our findings can provide some new understanding of the molecular regulatory network of petal development and floral morphology formation, as well as the differentiation of disc and ray florets in sunflower.
Keywords: Floral development; MADS-box genes; Petal prolongation; Sunflower; Symmetry.
© 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla ER, Benítez M, Corvera-Poiré A, Chaos Cador Á, de Folter S, Gamboa de Buen A, Garay-Arroyo A, García-Ponce B, Jaimes-Miranda F, Pérez-Ruiz RV, Piñeyro-Nelson A, Sánchez-Corrales YE. Flower development. The Arabidopsis Book/American Society of Plant Biologists. 2010;8(1):e0127. doi: 10.1199/tab.0127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Celedón-Neghme C, Gonzáles WL, Gianoli E. Cost and benefits of attractive floral traits in the annual species Madia sativa (Asteraceae) Evolutionary Ecology. 2007;21(2):247–257. doi: 10.1007/s10682-006-9002-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

