Evolution of protective SARS-CoV-2-specific B and T cell responses upon vaccination and Omicron breakthrough infection
- PMID: 38974469
- PMCID: PMC11225850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110138
Evolution of protective SARS-CoV-2-specific B and T cell responses upon vaccination and Omicron breakthrough infection
Abstract
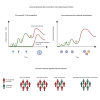
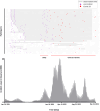
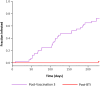
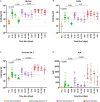
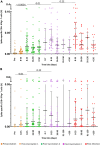
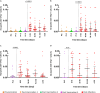
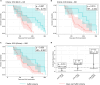
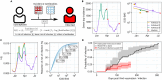
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron breakthrough infection (BTI) induced better protection than triple vaccination. To address the underlying immunological mechanisms, we studied antibody and T cell response dynamics during vaccination and after BTI. Each vaccination significantly increased peak neutralization titers with simultaneous increases in circulating spike-specific T cell frequencies. Neutralization titers significantly associated with a reduced hazard rate for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Yet, 97% of triple vaccinees became SARS-CoV-2 infected. BTI further boosted neutralization magnitude and breadth, broadened virus-specific T cell responses to non-vaccine-encoded antigens, and protected with an efficiency of 88% from further infections by December 2022. This effect was then assessed by utilizing mathematical modeling, which accounted for time-dependent infection risk, the antibody, and T cell concentration at any time point after BTI. Our findings suggest that cross-variant protective hybrid immunity induced by vaccination and BTI was an important contributor to the reduced virus transmission observed in Bavaria in late 2022 and thereafter.
Keywords: immunology; microbiology; virology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Flechsler J., Eberle U., Dangel A., Hepner S., Wimmer C., Lutmayr J., Konrad R., Berger C., Weise L., Sprenger A., et al. Molecular SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in Bavaria shows no Omicron transmission before the end of November 2021. Infection. 2022;50:761–766. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01767-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Varianten bei COVID-19 Patienten in Bayern. 2022. https://www.bay-voc.lmu.de/surveillance.xhtml
-
- Petrone D., Mateo-Urdiales A., Sacco C., Riccardo F., Bella A., Ambrosio L., Lo Presti A., Di Martino A., Ceccarelli E., Del Manso M., et al. Reduction of the risk of severe COVID-19 due to Omicron compared to Delta variant in Italy (November 2021 - February 2022) Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023;129:135–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

