A Prognostic Model Incorporating Relevant Peripheral Blood Inflammation Indicator to Predict Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster
- PMID: 38974827
- PMCID: PMC11225992
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S466939
A Prognostic Model Incorporating Relevant Peripheral Blood Inflammation Indicator to Predict Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster
Abstract
Objective: To determine the risk of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in patients with acute herpes zoster (HZ), this study developed and validated a novel clinical prediction model by incorporating a relevant peripheral blood inflammation indicator.
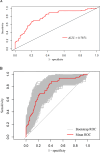
Methods: Between January 2019 and June 2023, 209 patients with acute HZ were categorized into the PHN group (n = 62) and the non-PHN group (n = 147). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify risk factors serving as independent predictors of PHN development. Subsequently, a nomogram prediction model was established, and the discriminative ability and calibration were evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic curve, calibration plots, and decision curve analysis (DCA). The nomogram model was internally verified through the bootstrap test method.
Results: According to univariate logistic regression analyses, five variables, namely age, hypertension, acute phase Numeric Rating Scale (NRS-11) score, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and systemic immune inflammation index, were significantly associated with PHN development. Multifactorial analysis further unveiled that age (odds ratio (OR) [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 2.309 [1.163-4.660]), acute phase NRS-11 score (OR [95% CI]: 2.837 [1.294-6.275]), and PLR (OR [95% CI]: 1.015 [1.010-1.022]) were independent risk factors for PHN. These three predictors were integrated to establish the prediction model and construct the nomogram. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for predicting the PHN risk was 0.787, and the AUC of internal validation determined using the bootstrap method was 0.776. The DCA and calibration curve also indicated that the predictive performance of the nomogram model was commendable.
Conclusion: In this study, a risk prediction model was developed and validated to accurately forecast the probability of PHN after HZ, thereby demonstrating favorable discrimination, calibration, and clinical applicability.
Keywords: nomogram; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; postherpetic neuralgia; risk factors.
© 2024 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Nomogram Model for Predicting Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Herpes Zoster: A Prospective Study.Pain Physician. 2024 Nov;27(8):E843-E850. Pain Physician. 2024. PMID: 39621984
-
Analysis of Risk Factors and Development and Validation of a Dynamic Nomogram for Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Retrospective Study.J Pain Res. 2024 Nov 20;17:3935-3948. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S483531. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39583189 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Prediction Model and Corresponding Scoring Table for Postherpetic Neuralgia Using Six Machine Learning Algorithms: A Retrospective Study.Pain Ther. 2024 Aug;13(4):883-907. doi: 10.1007/s40122-024-00612-7. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Pain Ther. 2024. PMID: 38834881 Free PMC article.
-
Management of herpes zoster (shingles) and postherpetic neuralgia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Mar;5(3):551-9. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.3.551. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15013924 Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of independent risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):12181-12189. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3028. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 35016460
Cited by
-
Effects of pulsed radiofrequency combined with ozone on zoster-associated pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Med Gas Res. 2026 Mar 1;16(1):76-81. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00150. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Med Gas Res. 2026. PMID: 40580192 Free PMC article.
-
A Nomogram Model Integrating Inflammation Markers for Predicting the Risk of Recurrent Sciatica After Selective Nerve Root Blocks.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Apr 12;18:1279-1289. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S503360. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 40242298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- H-L L, Gong G, Wang J-L, F-B L. Analysis of risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia in patients with postmalignancy herpes zoster. Pain Physician. 2023;26(4):E397–E403. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

