Nutritional aphrodisiacs: Biochemistry and Pharmacology
- PMID: 38974844
- PMCID: PMC11225857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100783
Nutritional aphrodisiacs: Biochemistry and Pharmacology
Abstract
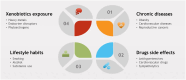
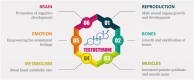
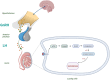
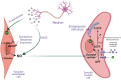
In 2022, the global prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) was estimated to be at least 150 million cases. This number is greatly suspected to be underestimate as most men withhold information about ED. Also, about 15% of world population have infertility troubles, and male factors are responsible for almost half of these cases. Studies have shown that the quality of semen has decreased in the past several decades owing to various health factors and environmental toxicants. The current medical interventions involve the inhibition of phosphodiesterase 5 which suffer from serious side effects and costly. One of the popular and most sought interventions are the natural and nutritional remedies as they are foods in essence and potentially with no harm to the body. Therefore, the goal of this paper is to provide a review of the most common nutritional aphrodisiacs with increasing libido and fertility highlighting the potential active constituents as well as the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Aphrodisiac foods; Aromatase inhibitors; Erectile dysfunction; Infertility; Testosterone.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Medicinal plants as a potential source of Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113536. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113536. Epub 2020 Nov 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33137431 Review.
-
Natural aphrodisiacs.J Sex Med. 2010 Jan;7(1 Pt 1):39-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01521.x. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Sex Med. 2010. PMID: 19796015 Review.
-
Association Between Infertility and Sexual Dysfunction in Men and Women.Sex Med Rev. 2016 Oct;4(4):353-365. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Sex Med Rev. 2016. PMID: 27872029 Review.
-
Erectile Dysfunction and Decreased Libido in Klinefelter Syndrome: A Prevalence Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Study.J Sex Med. 2021 Jun;18(6):1053-1064. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.03.078. Epub 2021 May 20. J Sex Med. 2021. PMID: 34023236 Review.
-
Fertility Related Quality of Life, Gonadal Function and Erectile Dysfunction in Male Partners of Couples with Unexplained Infertility.J Urol. 2019 Aug;202(2):379-384. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000205. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30835629 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Akhuetie J.O., Oyeyemi M.O., Oloye A.A. Studies on crude powder and ethanolic extract of Citrullus lanatus seeds: phytochemical analysis, effects on haemogram and some reproductive characteristics of male albino rats. Niger. Vet. J. 2018;39(2):133. doi: 10.4314/nvj.v39i2.5. - DOI
-
- Akinyemi A.J., Adedara I.A., Thome G.R., Morsch V.M., Rovani M.T., Mujica L.K.S., Duarte T., Duarte M., Oboh G., Schetinger M.R.C. Dietary supplementation of ginger and turmeric improves reproductive function in hypertensive male rats. Toxicol Rep. 2015;2:1357–1366. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.10.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

