The Effect of C-Reactive Protein/Lymphocyte Ratio (CLR) on PFS in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK4/6 Inhibitors: A Novel Biomarker
- PMID: 38974895
- PMCID: PMC11227876
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S464161
The Effect of C-Reactive Protein/Lymphocyte Ratio (CLR) on PFS in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK4/6 Inhibitors: A Novel Biomarker
Abstract
Objective: Hormone positive breast cancer is a tumor with high mortality. Combining antihormonal therapy with cyclin dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) has resulted in longer survival. The effect of inflammatory parameters such as c-reactive protein and c-reactive protein/lymphocyte ratio (CLR) on efficacy and survival in CDK4/6i treatment is unknown. In our study, we aimed to investigate the role of CLR and some parameters in predicting progression-free survival (PFS) with CDK4/6i.
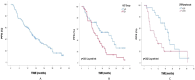
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 78 patients with denovo and recurrent metastatic breast cancer treated with CDK4/6i. Cut off values for the prediction of mortality by various numerical parameter scores were performed by ROC Curve analysis. The effect of clinical variables, inflammatory and histopathological parameters on survival was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier method.
Results: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and CLR were statistically significant in predicting mortality (p < 0.05). Ki67 and CLR were correlated with PFS. Age and CLR were correlated with OS (p < 0.05). CLR was statistically significant for both PFS (p = 0.022) and OS (p = 0.006).
Conclusion: In patients with metastatic hormone-positive breast cancer using CDK4/6i, low CLR and low Ki67 were correlated with longer PFS duration.
Keywords: C-reactivated protein/lymphocyte ratio; hormone-positive breast cancer; progression-free survival.
© 2024 Buyukbayram et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as prognostic factor in metastatic breast cancer treated with cyclin dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 19;12:1105587. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1105587. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36741710 Free PMC article.
-
Ratios of monocytes and neutrophils to lymphocytes in the blood predict benefit of CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment in metastatic breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 2;13(1):21262. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47874-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38040730 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical management of metastatic hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (MBC) after CDK 4/6 inhibitors: a retrospective single-institution study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Nov;196(1):229-237. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06713-1. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36045271 Free PMC article.
-
Overall survival and progression-free survival with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy in breast cancer: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Dec;25(23):7252-7267. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202112_27418. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34919224
-
Association of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 Inhibitors With Survival in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Oct 1;3(10):e2020312. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.20312. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33048129 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
C-reactive protein to lymphocyte ratio combined with clinical features to construct a predictive model for upper gastrointestinal bleeding due to peptic ulcer.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025 Apr 23;80:100644. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100644. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40273489 Free PMC article.
-
PIV and PILE scores predict the clinical outcome in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors.Int J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jul;30(7):1341-1354. doi: 10.1007/s10147-025-02770-w. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Int J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40257656
-
Associations of C-reactive protein to lymphocyte ratio and metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: evidence from NHANES 2017-2018.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 24;24(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03458-7. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39719591 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between C-reactive protein to lymphocyte ratio and the prevalence of chronic kidney disease in US adults: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 15;15:1469750. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1469750. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39882264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2019–2020. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials