Gonorrhea cluster detection in Manitoba, Canada: Spatial, temporal, and spatio-temporal analysis
- PMID: 38974897
- PMCID: PMC11222937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2024.05.009
Gonorrhea cluster detection in Manitoba, Canada: Spatial, temporal, and spatio-temporal analysis
Abstract
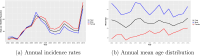
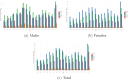
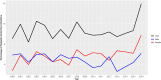
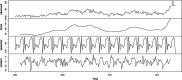
In Canada, Gonorrhea infection ranks as the second most prevalent sexually transmitted infection. In 2018, Manitoba reported an incidence rate three times greater than the national average. This study aims to investigate the spatial, temporal, and spatio-temporal patterns of Gonorrhea infection in Manitoba, using individual-level laboratory-confirmed administrative data provided by Manitoba Health from 2000 to 2016. Age and sex patterns indicate that females are affected by infections at younger ages compared to males. Moreover, there is an increase in repeated infections in 2016, accounting for 16% of the total infections. Spatial analysis at the 96 Manitoba regional health authority districts highlights significant positive spatial autocorrelation, demonstrating a clustered distribution of the infection. Northern districts of Manitoba and central Winnipeg were identified as significant clusters. Temporal analysis shows seasonal patterns, with higher infections in late summer and fall. Additionally, spatio-temporal analysis reveals clusters during high-risk periods, with the most likely cluster in the northern districts of Manitoba from January 2006 to June 2014, and a secondary cluster in central Winnipeg from June 2004 to November 2012. This study identifies that Gonorrhea infection transmission in Manitoba has temporal, spatial, and spatio-temporal variations. The findings provide vital insights for public health and Manitoba Health by revealing high-risk clusters and emphasizing the need for focused and localized prevention, control measures, and resource allocation.
Keywords: Cluster detection; Gonorrhea; Infectious disease; Spatial analysis; Spatio-temporal analysis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Bernstein K.T., Marcus J.L., Nieri G., Philip S.S., Klausner J.D. Rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia reinfection is associated with increased risk of HIV seroconversion. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2010;53:537–543. - PubMed
-
- Box G.E., Cox D.R. An analysis of transformations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society - Series B: Statistical Methodology. 1964;26:211–243.
-
- Box G.E., Jenkins G.M., Reinsel G.C., Ljung G.M. John Wiley & Sons; 2015. Time series analysis: Forecasting and control.
-
- Bush K.R., Henderson E.A., Dunn J., Read R.R., Singh A. Mapping the core: chlamydia and gonorrhea infections in calgary, Alberta. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 2008:291–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

