Golexanolone reduces glial activation in the striatum and improves non-motor and some motor alterations in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 38974902
- PMCID: PMC11224447
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1417938
Golexanolone reduces glial activation in the striatum and improves non-motor and some motor alterations in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) affects more than 6 million people worldwide. Along with motor impairments, patients and animal models exhibiting PD symptoms also experience cognitive impairment, fatigue, anxiety, and depression. Currently, there are no drugs available for PD that alter the progression of the disease. A body of evidence suggests that increased GABA levels contribute to the reduced expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and accompanying behavioral deficits. TH expression may be restored by blocking GABAA receptors. We hypothesized that golexanolone (GR3027), a well-tolerated GABAA receptor-modulating steroid antagonist (GAMSA), may improve Parkinson's symptoms in a rat model of PD.
Objectives: The aims of this study were to assess whether golexanolone can ameliorate motor and non-motor symptoms in a rat model of PD and to identify some underlying mechanisms.
Methods: We used the unilateral 6-OHDA rat model of PD. The golexanolone treatment started 4 weeks after surgery. Motor symptoms were assessed using Motorater and CatWalk tests. We also analyzed fatigue (using a treadmill test), anhedonia (via the sucrose preference test), anxiety (with an open field test), and short-term memory (using a Y maze). Glial activation and key proteins involved in PD pathogenesis were analyzed using immunohistochemistry and Western blot.
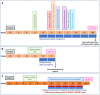
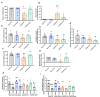
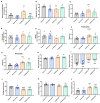
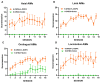
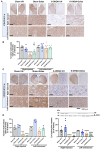
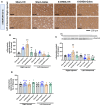
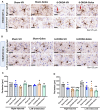
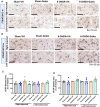
Results: Rats with PD showed motor incoordination and impaired locomotor gait, increased fatigue, anxiety, depression, and impaired short-term memory. Golexanolone treatment led to improvements in motor incoordination, certain aspects of locomotor gait, fatigue, anxiety, depression, and short-term memory. Notably, golexanolone reduced the activation of microglia and astrocytes, mitigated TH loss at 5 weeks after surgery, and prevented the increase of α-synuclein levels at 10 weeks.
Conclusions: Golexanolone may be useful in improving both motor and non-motor symptoms that adversely affect the quality of life in PD patients, such as anxiety, depression, fatigue, motor coordination, locomotor gait, and certain cognitive alterations.
Keywords: 6-OHDA model; GABAergic neurotransmission; Parkinson's disease; cognitive impairment; glial activation; motor impairment.
Copyright © 2024 Izquierdo-Altarejos, Arenas, Martínez-García, Vázquez, Mincheva, Doverskog, Blackburn, Bohnen, Llansola and Felipo.
Conflict of interest statement
TB is an independent Director of the Board of Umecrine Cognition AB. MD is employed by and has shares in Umecrine Cognition AB. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Golexanolone improves fatigue, motor incoordination and gait and memory in rats with bile duct ligation.Liver Int. 2024 Feb;44(2):433-445. doi: 10.1111/liv.15782. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Liver Int. 2024. PMID: 38010893
-
Golexanolone, a GABAA receptor modulating steroid antagonist, restores motor coordination and cognitive function in hyperammonemic rats by dual effects on peripheral inflammation and neuroinflammation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Nov;28(11):1861-1874. doi: 10.1111/cns.13926. Epub 2022 Jul 26. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35880480 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation alters GABAergic neurotransmission in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy, leading to motor incoordination. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1358323. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1358323. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38560359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pilot study of golexanolone, a new GABA-A receptor-modulating steroid antagonist, in patients with covert hepatic encephalopathy.J Hepatol. 2021 Jul;75(1):98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.012. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33894327 Clinical Trial.
-
New pharmacological options for treating advanced Parkinson's disease.Clin Ther. 2013 Oct;35(10):1640-52. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 24011636 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical efficacy and potential mechanisms of acupuncture for Parkinson's disease: the role of GABAergic signaling.Front Neurosci. 2025 Feb 19;19:1525486. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1525486. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40046435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agusti A., Hernández-Rabaza V., Balzano T., Taoro-Gonzalez L., Ibañez-Grau A., Cabrera-Pastor A., et al. . (2017). Sildenafil reduces neuroinflammation in cerebellum, restores GABAergic tone, and improves motor in-coordination in rats with hepatic encephalopathy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 23, 386–394. 10.1111/cns.12688 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

