Defective recovery of QT dispersion due to no-reflow following acute interventional therapy in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 38975003
- PMCID: PMC11223942
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-23-398
Defective recovery of QT dispersion due to no-reflow following acute interventional therapy in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested that adequate myocardial reperfusion after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can improve the inhomogeneity of myocardial repolarization. However, it remains unclear whether no-reflow (NR) following emergency PCI involves disadvantages related to ventricular repolarization indices. The present study aimed to determine the effect of NR on QT dispersion (QTd) in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and to evaluate the prognostic value of the relative reduction of QTd on ventricular arrhythmia events (VAEs).
Methods: A prospective case-control study was conducted. According to the inclusion criteria, 275 patients with STEMI who underwent primary PCI treatment at the First People's Hospital of Anqing affiliated to Anhui Medical University from January 2020 to May 2023 were enrolled. According to whether NR occurred during PCI, these patients were divided into two groups: an NR group and a non-NR group. Subsequently, the QT intervals were measured before and at 12 hours after PCI. Afterward, the QTd, corrected QTd (QTcd), and the relative reduction of QTd and QTcd 12 hours pre- and postprocedure (ΔQTd-R and ΔQTcd-R, respectively) were calculated. Finally, multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to predict the risk of VAE occurrence.
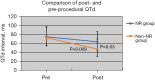
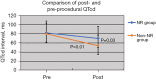
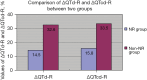
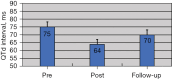
Results: In the non-NR group, there was a significant decrease from baseline in postprocedure QTd (48±17 vs. 73±22 ms; P=0.009) and QTcd (54±19 vs. 80±23 ms; P=0.01); in contrast, the NR group showed no significant difference in QTd (64±20 vs. 75±23 ms; P=0.58) or QTd (70±22 vs. 82±26 ms; P=0.45). Furthermore, the ΔQTd-R and ΔQTcd-R were both lower in the NR group than in the non-NR group (P<0.05); however, the rate of VAEs was higher in the NR group than in the non-NR group (15.2% vs. 6.2%; P=0.02). The multivariable logistic regression analysis results revealed that each increase of 12% in ΔQTcd-R was an independent predictor of VAEs (odds ratio: 0.547; 95% confidence interval: 0.228-0.976).
Conclusions: The NR phenomenon following primary PCI in patients with STEMI leads to the defective recovery of QTd and QTcd. Furthermore, ΔQTcd-R can be viewed as an effective indicator for evaluating the myocardial repolarization inhomogeneity, and short-term clinical outcomes.
Keywords: QT dispersion (QTd); ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI); no-reflow (NR); percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI); ventricular arrhythmias events.
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-23-398/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of reperfusion strategy on QT dispersion in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Impact on in-hospital arrhythmia.World J Cardiol. 2023 Mar 26;15(3):106-115. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i3.106. World J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37033680 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of QT dispersion in patients with ST elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI) before and after treatment by streptokinase versus primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Nov 23;20(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01767-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 33228554 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of nicorandil on ventricular arrhythmia in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction underwent emergent percutaneous coronary intervention treatment].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 24;45(8):701-705. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2017.08.016. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28851188 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Comparison between QT Interval Parameters in Type 2 Diabetic and Nondiabetic Patients with Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2014;9(4):166-73. Epub 2014 Jul 6. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2014. PMID: 25870641 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between the Serum Uric Acid to Albumin Ratio and the No-Reflow Phenomenon After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Apr 4;17(4):e81712. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81712. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40322371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sema4D combined with electrocardiographic parameters for predicting STEMI prognosis: Development and validation of a nomogram model.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 11;104(28):e43236. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043236. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40660574 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Endurance Training and High-Intensity Resistance Training on Pulse Wave Velocity and QT Dispersion.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;13(2):161. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13020161. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857188 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome.Children (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;12(4):474. doi: 10.3390/children12040474. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310095 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
