Intracranial cerebrovascular lesions on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 38975060
- PMCID: PMC11225518
- DOI: 10.25259/JCIS_16_2024
Intracranial cerebrovascular lesions on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
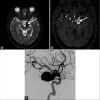
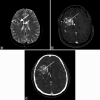
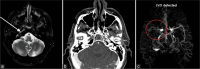
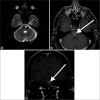
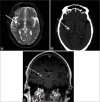
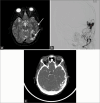
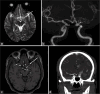
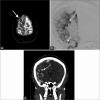
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain has been implemented to evaluate multiple intracranial pathologies. Non-contrast T2-weighted images are a routinely acquired sequence in almost all neuroimaging protocols. It is not uncommon to encounter various cerebrovascular lesions incidentally on brain imaging. Neuroradiologists should evaluate the routine T2-weighted images for incidental cerebrovascular lesions, irrespective of the primary indication of the study. Vascular structures typically demonstrate a low signal flow-void on the T2-weighted images. In our experience, large cerebrovascular abnormalities are easily visible to a typical neuroradiologist. In this article, we present the spectrum of the characteristic imaging appearance of various intracranial cerebrovascular lesions on routine non-contrast T2-weighted MRI. These include aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, arterial occlusion, capillary telangiectasia, cavernous malformation, dural arteriovenous fistula, moyamoya, proliferative angiopathy, and vein of Galen malformation.
Keywords: Cerebrovascular; Incidental findings; Magnetic resonance imaging; Non-invasive imaging; Opportunistic screening.
© 2024 Published by Scientific Scholar on behalf of Journal of Clinical Imaging Science.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
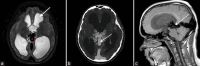
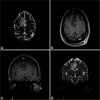
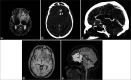
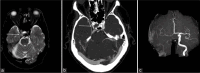
Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic imaging of hemangiomas in the brain].Brain Nerve. 2011 Jan;63(1):5-15. Brain Nerve. 2011. PMID: 21228443 Review. Japanese.
-
Comparative Analysis of Volumetric High-Resolution Heavily T2-Weighted MRI and Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MRA in the Evaluation of Spinal Vascular Malformations.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Sep;40(9):1601-1606. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6164. Epub 2019 Aug 22. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 31439626 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of SWI sequences compared to T2*-weighted gradient echo sequences in the detection of cerebral cavernous malformations in the familial form.Neuroradiol J. 2016 Oct;29(5):326-35. doi: 10.1177/1971400916665376. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Neuroradiol J. 2016. PMID: 27549150 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular disease and syndromes: Diagnosis and therapy in children.Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;176:305-323. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64034-5.00015-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33272401 Review.
-
Hypointense thrombus on T2-weighted MR imaging: a potential pitfall in the diagnosis of dural sinus thrombosis.Eur J Radiol. 2002 Feb;41(2):147-52. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00365-5. Eur J Radiol. 2002. PMID: 11809544
References
-
- Sato K, Hijikata Y, Omura N, Miki T, Kakita H, Yoshida T, et al. Usefulness of three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition MRI of large vessel occlusion for detecting occluded middle cerebral artery and internal carotid artery before acute mechanical thrombectomy. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2021;23:201–9. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2020.10.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
