From inflammatory signaling to neuronal damage: Exploring NLR inflammasomes in ageing neurological disorders
- PMID: 38975145
- PMCID: PMC11226848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32688
From inflammatory signaling to neuronal damage: Exploring NLR inflammasomes in ageing neurological disorders
Abstract
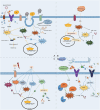
The persistence of neuronal degeneration and damage is a major obstacle in ageing medicine. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors detect environmental stressors and trigger the maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can cause neuronal damage and accelerate cell death. NLR (NOD-like receptors) inflammasomes are protein complexes that contain NOD-like receptors. Studying the role of NLR inflammasomes in ageing-related neurological disorders can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of neurodegeneration. This includes investigating their activation of inflammasomes, transcription, and capacity to promote or inhibit inflammatory signaling, as well as exploring strategies to regulate NLR inflammasomes levels. This review summarizes the use of NLR inflammasomes in guiding neuronal degeneration and injury during the ageing process, covering several neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, stroke, and peripheral neuropathies. To improve the quality of life and slow the progression of neurological damage, NLR-based treatment strategies, including inhibitor-related therapies and physical therapy, are presented. Additionally, important connections between age-related neurological disorders and NLR inflammasomes are highlighted to guide future research and facilitate the development of new treatment options.
Keywords: Ageing; NLR inflammasomes; Neurological disorders; Treatment.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[A role of inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of neurological and mental diseases].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2018;118(12):81-91. doi: 10.17116/jnevro201811812181. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2018. PMID: 30698567 Russian.
-
Therapeutic role of inflammasome inhibitors in neurodegenerative disorders.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jan;91:771-783. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33157255 Review.
-
Structural Mechanisms in NLR Inflammasome Assembly and Signaling.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;397:23-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41171-2_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27460803
-
NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: A review of their canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019 Jul 30;670:4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019. PMID: 30772258 Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
References
-
- Xue Y., Tuipulotu D.E., Tan W.H., Kay C., Man S.M. Emerging activators and regulators of inflammasomes and pyroptosis. Trends Immunol. 2019;40:1035–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

