The expression of MIR125B transcripts and bone phenotypes in Mir125b2-deficient mice
- PMID: 38976685
- PMCID: PMC11230526
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304074
The expression of MIR125B transcripts and bone phenotypes in Mir125b2-deficient mice
Abstract
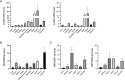
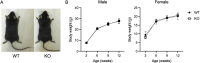
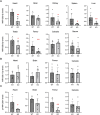
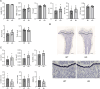
MIR125B, particularly its 5p strand, is apparently involved in multiple cellular processes, including osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. Given that MIR125B is transcribed from the loci Mir125b1 and Mir125b2, three mature transcripts (MIR125B-5p, MIR125B1-3p, and MIR125B2-3p) are generated (MIR125B-5p is common to both); however, their expression profiles and roles in the bones remain poorly understood. Both primary and mature MIR125B transcripts were differentially expressed in various organs, tissues, and cells, and their expression patterns did not necessarily correlate in wild-type (WT) mice. We generated Mir125b2 knockout (KO) mice to examine the contribution of Mir125b2 to MIR125B expression profiles and bone phenotypes. Mir125b2 KO mice were born and grew normally without any changes in bone parameters. Interestingly, in WT and Mir125b2 KO, MIR125B-5p was abundant in the calvaria and bone marrow stromal cells. These results indicate that the genetic ablation of Mir125b2 does not impinge on the bones of mice, attracting greater attention to MIR125B-5p derived from Mir125b1. Future studies should investigate the conditional deletion of Mir125b1 and both Mir125b1 and Mir125b2 in mice.
Copyright: © 2024 Ogasawara et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
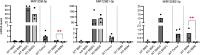
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

