Triple-drug therapy with ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and albendazole for the acceleration of lymphatic filariasis elimination in Kenya: Programmatic implementation and results of the first impact assessment
- PMID: 38976718
- PMCID: PMC11257386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011942
Triple-drug therapy with ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and albendazole for the acceleration of lymphatic filariasis elimination in Kenya: Programmatic implementation and results of the first impact assessment
Abstract
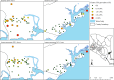
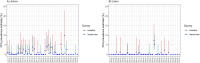
The World Health Organization (WHO) endorsed the use of triple-drug mass drug administration (MDA) regimen with ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine (DEC) and albendazole (commonly abbreviated as IDA) to accelerate the elimination of lymphatic filariasis (LF) as a public health problem in settings where onchocerciasis is not co-endemic. The National Programme for Elimination of LF (NPELF) in Kenya was among the first adopters of the IDA-MDA and two annual rounds were provided in 2018 and 2019 to the residents of Lamu County and Jomvu sub-County in the coast region. This study documented the feasibility of successfully delivering the two rounds of IDA-MDA. An operational research study was undertaken to determine efficient sampling strategies, indicators, and the appropriate population groups that could be used for the monitoring and evaluation of LF programs using IDA-MDA for the elimination of the disease as a public health problem. Two cross-sectional surveys were conducted at baseline in 2018 before IDA-MDA and an impact assessment 17 months after the second round of IDA-MDA. The reported epidemiological treatment coverage was at least 80% in all implementation units during each round of IDA-MDA. Blood samples were tested for filarial antigenemia using commercial Filariasis Test Strips (FTS) and any individual found to be positive was tested again at night for the presence of microfilariae in finger prick blood smears using microscopy. The overall prevalence of circulating filarial antigen (CFA) was relatively low at the baseline survey with Jomvu having 1.39% (95% CI: 0.91, 2.11) and Lamu having 0.48% (95% CI: 0.21, 1.13). Significant reduction in CFA prevalence was observed during the impact assessment after the two annual rounds of mass treatment. The overall relative reduction (%) in CFA prevalence following the two rounds of MDA with IDA was significant in both Jomvu (52.45%, Z = -2.46, P < 0.02) and Lamu (52.71%, Z = -1.97, P < 0.05). Heterogeneity, however, was observed in the CFA prevalence reduction between random and purposive clusters, as well as between adult and child populations. The results of the impact assessment survey offered strong evidence that it was safe to stop the IDA-MDA in the two EUs because transmission appears to have been interrupted. It is also important to implement a post-treatment surveillance system which would enable efficient detection of any recrudescence of LF transmission at a sub-evaluation unit level. Our findings show that IDA-MDA may be considered for acceleration of LF elimination in other settings where onchocerciasis is not co-endemic.
Copyright: © 2024 Njenga et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis: progress report, 2021. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2022;97(41):513–24
-
- WHO. Global programme to eliminate lymphatic filariasis: progress report, 2019. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2020;95(43):509–24.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

