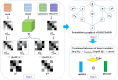
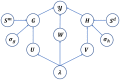
Kernel Bayesian logistic tensor decomposition with automatic rank determination for predicting multiple types of miRNA-disease associations
- PMID: 38976761
- PMCID: PMC11257412
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012287
Kernel Bayesian logistic tensor decomposition with automatic rank determination for predicting multiple types of miRNA-disease associations
Abstract
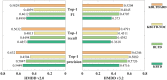
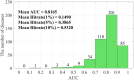
Identifying the association and corresponding types of miRNAs and diseases is crucial for studying the molecular mechanisms of disease-related miRNAs. Compared to traditional biological experiments, computational models can not only save time and reduce costs, but also discover potential associations on a large scale. Although some computational models based on tensor decomposition have been proposed, these models usually require manual specification of numerous hyperparameters, leading to a decrease in computational efficiency and generalization ability. Additionally, these linear models struggle to analyze complex, higher-order nonlinear relationships. Based on this, we propose a novel framework, KBLTDARD, to identify potential multiple types of miRNA-disease associations. Firstly, KBLTDARD extracts information from biological networks and high-order association network, and then fuses them to obtain more precise similarities of miRNAs (diseases). Secondly, we combine logistic tensor decomposition and Bayesian methods to achieve automatic hyperparameter search by introducing sparse-induced priors of multiple latent variables, and incorporate auxiliary information to improve prediction capabilities. Finally, an efficient deterministic Bayesian inference algorithm is developed to ensure computational efficiency. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets show that KBLTDARD has better Top-1 precision, Top-1 recall, and Top-1 F1 for new type predictions, and higher AUPR, AUC, and F1 values for new triplet predictions, compared to other state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, case studies demonstrate the efficiency of KBLTDARD in predicting multiple types of miRNA-disease associations.
Copyright: © 2024 Ma, Ma. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials