Sediment subduction in Hadean revealed by machine learning
- PMID: 38976765
- PMCID: PMC11287277
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2405160121
Sediment subduction in Hadean revealed by machine learning
Abstract
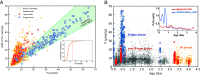
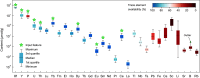
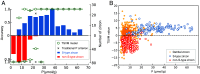
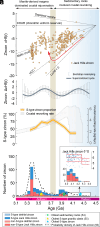
Due to the scarcity of rock samples, the Hadean Era predating 4 billion years ago (Ga) poses challenges in understanding geological processes like subaerial weathering and plate tectonics that are critical for the evolution of life. The Jack Hills zircon from Western Australia, the primary Hadean samples available, offer valuable insights into magma sources and tectonic genesis through trace element signatures. However, a consensus on these signatures has not been reached. To address this, we developed a machine learning classifier capable of deciphering the geochemical fingerprints of zircon. This allowed us to identify the oldest detrital zircon originating from sedimentary-derived "S-type" granites. Our results indicate the presence of S-type granites as early as 4.24 Ga, persisting throughout the Hadean into the Archean. Examining global detrital zircon across Earth's history reveals consistent supercontinent-like cycles from the present back to the Hadean. These findings suggest that a significant amount of Hadean continental crust was exposed, weathered into sediments, and incorporated into the magma sources of Jack Hills zircon. Only the early operation of both subaerial weathering and plate subduction can account for the prevalence of S-type granites we observe. Additionally, the periodic evolution of S-type granite proportions implies that subduction-driven tectonic cycles were active during the Hadean, at least around 4.2 Ga. The evidence thus points toward an early Earth resembling the modern Earth in terms of active tectonics and habitable surface conditions. This suggests the potential for life to originate in environments like warm ponds rather than extreme hydrothermal settings.
Keywords: Hadean; S-type granite; machine learning; subduction; zircon.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Palin R. M., Secular change and the onset of plate tectonics on Earth. Earth-Sci. Rev. 207, 103172 (2020). 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103172. - DOI
-
- Maruyama S., Santosh M., Azuma S., Initiation of plate tectonics in the Hadean: Eclogitization triggered by the ABEL Bombardment. Geosci. Front. 9, 1033–1048 (2018).
-
- Tang M., Chen K., Rudnick R. L., Archean upper crust transition from mafic to felsic marks the onset of plate tectonics. Science 351, 372–375 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Shirey S. B., Richardson S. H., Start of the Wilson cycle at 3 GA shown by diamonds from subcontinental mantle. Science 333, 434–436 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Stern R. J., Leybourne M. I., Tsujimori T., Kimberlites and the start of plate tectonics. Geology 44, 799–802 (2016).

