Agreement and repeatability of scotopic pupil size measurement with the 2WIN-S portable refractor in Chinese adults
- PMID: 38977905
- PMCID: PMC11231274
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66540-w
Agreement and repeatability of scotopic pupil size measurement with the 2WIN-S portable refractor in Chinese adults
Abstract
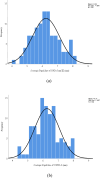
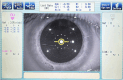
To assess the agreement and repeatability of scotopic pupil size measurement using 2WIN-S (Adaptica, Padova, Italy) portable refractor in Chinese adults. This prospective non-randomized open-label controlled study assessed the scotopic pupil size of 100 right eyes using OPD-Scan III (Optical path difference) (Nidek Technologies, Gamagori, Japan) and 2WIN-S. OPD-Scan III and 2WIN-S measure pupil size using infrared light and detector, while 2WIN-S measures bilateral eyes simultaneously, OPD-Scan III measures unilateral eyes individually. Participants were first measured once using OPD-Scan III and two consecutive measurements were performed using 2WIN-S after 15 min of rest interval. The primary outcome was to evaluate the agreement between 2WIN-S and OPD-Scan III, and the secondary outcome was to evaluate the repeatability of 2WIN-S. Scotopic pupil size of 100 right eyes of 100 adults (28 male and 72 female) aged 18-53 years (mean 36 ± 12 years) was assessed using OPD-Scan III and 2WIN-S, respectively. The mean scotopic pupil size of OPD-Scan III and 2WIN-S was recorded to be 6.24 ± 0.88 mm and 6.27 ± 0.81 mm, respectively. For the mean scotopic pupil size of OPD-Scan III and 2WIN-S the difference was - 0.03 mm (95%CI - 0.10 to 0.04 mm), p = 0.445, the 95% limits of agreement (LOA) was - 0.71 to 0.66 mm. ICC between the two devices was 0.92 (95% CI 0.88-0.94) (ICC > 0.9 indicates excellent consistency). Coefficients of repeatability (CoR) of 2WIN-S was 0.37, which has a high repeatability. For the mean scotopic pupil size of 2WIN-S of the repeated measurements, the difference was -0.04 mm (95%CI - 0.08 to 0.01 mm), p = 0.019, the 95% limits of agreement (LOA) was - 0.41 to 0.32 mm, with a narrow LOA. However, the majority of the variations were less than ± 0.50 mm (98% of scotopic pupil size measurements were below this threshold), within the clinically acceptable range (± 0.50 mm). Our study showed excellent agreement between 2WIN-S and OPD-Scan III (ICC > 0.9) and a good repeatability of 2WIN-S (CoR = 0.37). This study suggests a novel technique for measuring pupillary responses in low light conditions, which can be considered an alternative to OPD-Scan III in clinical settings.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Repeatability of pupil size measurements with NIDEK OPD-Scan III in myopic children.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021 Mar;41(2):431-436. doi: 10.1111/opo.12774. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021. PMID: 33294971
-
Comparison of 2 multiple-measurement infrared pupillometers to determine scotopic pupil diameter.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006 Nov;32(11):1926-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.07.019. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006. PMID: 17081898
-
Comparing School-Aged Refraction Measurements Using the 2WIN-S Portable Refractor in Relation to Cycloplegic Retinoscopy: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Ophthalmol. 2021 May 21;2021:6612476. doi: 10.1155/2021/6612476. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34094595 Free PMC article.
-
AcuTarget measurements: repeatability and comparison to OPD-Scan III.J Refract Surg. 2014 Mar;30(3):180-5. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20140217-05. J Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 24763722
-
Repeatability of Pentacam-derived intraocular lens decentration measurements and the level of agreement with OPD-Scan III: A prospective observational case series.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 22;19(3):e0299064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299064. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38517869 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Factors Affecting Ray Trace LASIK Data Acquisition in Clinical Practice: Options for Addressing Accommodation.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 3;19:2079-2089. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S524774. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40625637 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

