Pharmacological Gq inhibition induces strong pulmonary vasorelaxation and reverses pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 38977926
- PMCID: PMC11319782
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-024-00096-0
Pharmacological Gq inhibition induces strong pulmonary vasorelaxation and reverses pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
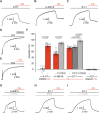
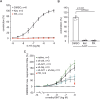
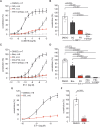
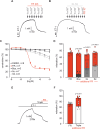
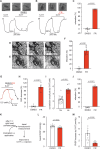
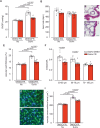
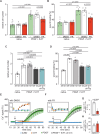
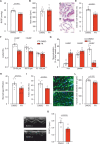
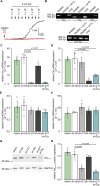
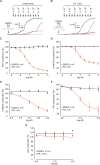
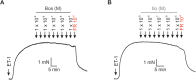
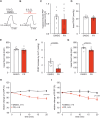
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease with limited survival. Herein, we propose the pharmacological inhibition of Gq proteins as a novel concept to counteract pulmonary vasoconstriction and proliferation/migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) in PAH. We demonstrate that the specific pan-Gq inhibitor FR900359 (FR) induced a strong vasorelaxation in large and small pulmonary arteries in mouse, pig, and human subjects ex vivo. Vasorelaxation by FR proved at least as potent as the currently used triple therapy. We also provide in vivo evidence that local pulmonary application of FR prevented right ventricular systolic pressure increase in healthy mice as well as in mice suffering from hypoxia (Hx)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH). In addition, we demonstrate that chronic application of FR prevented and also reversed Sugen (Su)Hx-induced PH in mice. We also demonstrate that Gq inhibition reduces proliferation and migration of PASMCs in vitro. Thus, our work illustrates a dominant role of Gq proteins for pulmonary vasoconstriction as well as remodeling and proposes direct Gq inhibition as a powerful pharmacological strategy in PH.
Keywords: Gq Inhibition; Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension; Vasoconstriction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bai Y, Krishnamoorthy N, Patel KR, Rosas I, Sanderson MJ, Ai X (2016) Cryopreserved human precision-cut lung slices as a bioassay for live tissue banking. A viability study of bronchodilation with bitter-taste receptor agonists. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 54:656–663 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0290MA - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

