Explaining inequity in knowledge, attitude, and services related to HIV/AIDS: a systematic review
- PMID: 38978024
- PMCID: PMC11229290
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-19329-5
Explaining inequity in knowledge, attitude, and services related to HIV/AIDS: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Equitable service provision and coverage are important responses to end the threat of the HIV/AIDS pandemic. Understanding inequity supports policies and programmes to deliver tailored interventions. There is continuous evidence generation on inequity in HIV/AIDS services. However, there was a lack of evidence on the global picture of inequity in behavioural and biomedical services related to HIV/AIDS. This systematic review assessed inequities in knowledge, attitude, HIV testing, and ART coverage across individual-level social groups and multiple (dis)advantage categories.
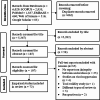
Methods: This review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guideline, with a PROSPERO registration number CRD42024521247. The risk of bias was assessed by using Hoy et al's and Joanna Brigg's quality appraisal checklists for cross-sectional quantitative and qualitative studies, respectively. The search date was from inception to the final database search date (May 29, 2023). The included articles were either quantitative or qualitative studies. We used mixed-methods approach to analyse the data from the review articles. Quantitative descriptive analysis was conducted to estimate frequency of articles published from different countries around the world. Qualitative content analysis of the findings from the original studies was conducted using the PROGRESS plus framework which stands for: place of residence, occupation or employment status, gender, religion, education status, socioeconomic status, and social capital.
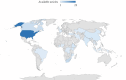
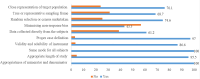
Results: Out of 6,029 articles that were accessed and screened, only 72 articles met the inclusion criteria. More articles on HIV-related equity in knowledge, attitude, testing, and ART were published in developed countries than in developing countries. Individuals from higher-income households had better knowledge about HIV/AIDS. Unfavourable attitudes towards people living with HIV and HIV/AIDS-associated stigma were common among women. HIV/AIDS service coverage (HIV testing or ART coverage) was higher among richer and urban residents. HIV/AIDS-associated stigma and lower levels of knowledge about HIV/AIDS were observed among multiple disadvantageous groups due to the intersection of two or more identities.
Conclusions: The current review revealed that there have been disparities in HIV/AIDS services between social classes. Ending service disparity towards the global threat of HIV/AIDS demands tailored interventions based on socially disadvantaged groups (e.g., poor, rural dwellers, and women) and intersectional determinants. There is a need to understand the deep-rooted causes of inequity and the challenges that an equity-oriented system faces over time. More studies on inequity are needed, including intersectional inequity, which has been rarely studied in developing countries.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Attitude; Discrimination; Disparity; Equality; Equity; HIV testing; Knowledge; Review; Stigma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
To what extent is equity entrenched in HIV/AIDS-related policy documents in Ethiopia? A policy content analysis.Health Res Policy Syst. 2025 May 22;23(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12961-025-01292-1. Health Res Policy Syst. 2025. PMID: 40405179 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of social protection on gender equality in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review of reviews.Campbell Syst Rev. 2022 May 25;18(2):e1240. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1240. eCollection 2022 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36913187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determinants of effective interventions for HIV prevention, treatment, and care to address inequitable HIV outcomes among Black Women of African Descent (BWAD) in High-Income Countries: Systematic review protocol.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 11;19(6):e0304255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304255. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38861503 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-COVID-19 Medication Adherence Among HIV/AIDS Patients in Belize: A Case for Consolidating Education and Monitoring.AIDS Res Treat. 2025 May 25;2025:5552340. doi: 10.1155/arat/5552340. eCollection 2025. AIDS Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40458538 Free PMC article.
-
Factors related to loss to follow-up among people living with HIV: a systematic review.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2025 Aug 18;67:e53. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202567053. eCollection 2025. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2025. PMID: 40834146 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: World AIDS Day 2022: putting ourselves to the test: achieving equity to end HIV.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 13;12:1478645. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1478645. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39346587 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Experiences, Challenges, and Needs of People Living with HIV in Hunan Province, China: A Qualitative Study.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Mar 7;18:1405-1421. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S512278. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40070600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doyle MW, Stiglitz JE. Eliminating extreme inequality: a sustainable development goal, 2015–2030. Ethics Int Affairs. 2014;28(1):5–13. doi: 10.1017/S0892679414000021. - DOI
-
- UNAIDS. The Sustainable Development Goals and the HIV response. Geneva, Switzerland: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous