The Relationship between the complement system and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38978073
- PMCID: PMC11229295
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03360-3
The Relationship between the complement system and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) events and CV mortality. Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis is independently associated with rates of incident CV events among patients with RA. The complement system has been related to both the etiopathogenesis of RA and CV disease. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the association between a comprehensive assessment of the complement system and carotid intima media thickness and carotid plaque in patients with RA.
Methods: 430 patients with RA were recruited. Functional assays of the three pathways of the complement system, utilizing new-generation techniques, were assessed. Additionally, serum levels of individual components of the complement system belonging to the three pathways were measured: C1q (classical), lectin (lectin), C2, C4, and C4b (classical and lectin), factor D and properdin (alternative), C3 and C3a (common), C5, C5a, and C9 (terminal), as well as regulators factor I and C1-inhibitor. Subclinical carotid atherosclerosis was evaluated by ultrasonography. Multivariable linear regression analysis was conducted to investigate the association between the complement system and carotid intima media thickness and carotid plaque.
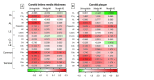
Results: After multivariable adjustment, which included traditional CV risk factors and disease-related data, C3a and C5a exhibited significant positive correlations with carotid intima media thickness. Additionally, higher values of C1-inhibitor, properdin, C3, C5, and C5a were independently associated with the presence of carotid plaque.
Conclusion: The complement system and subclinical carotid atherosclerosis are linked in patients with RA.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Carotid plaque; Complement system; Intima media thickness; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests related to this study. Nevertheless, Professor MA Gonzalez-Gay and Dr. Iván Ferraz-Amaro would like to acknowledge that they have received grants/research supports from Abbott, MSD, Jansen and Roche, as well as consultation fees from company-sponsored speakers bureaus associated with Abbott, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Celgene and MSD.
Figures
References
-
- Castañeda S, Nurmohamed MT, González-Gay MA. Cardiovascular disease in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2024 Apr 15];30:851–69. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27964792/. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Michaud K. The risk of myocardial infarction and pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic myocardial infarction predictors in rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort and nested case-control analysis. Arthritis Rheum [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2024 Mar 31];58:2612–21. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18759273/. - PubMed
-
- Aviña-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, Etminan M, Esdaile JM, Lacaille D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum [Internet]. 2008 [cited 2024 Mar 31];59:1690–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19035419/. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Gay MA, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Piñeiro A, Garcia-Porrua C, Testa A, Llorca J. High-grade C-reactive protein elevation correlates with accelerated atherogenesis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [Internet]. Journal of Rheumatology. J Rheumatol; 2005 [cited 2021 Sep 4]. pp. 1219–23. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15996055/. - PubMed
-
- López-Mejías R, Castañeda S, González-Juanatey C, Corrales A, Ferraz-Amaro I, Genre F et al. Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The relevance of clinical, genetic and serological markers. Autoimmun Rev [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2024 Apr 29];15:1013–30. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27490206/. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

