Implementation factors of tuberculosis control program in primary healthcare settings in China: a mixed-methods using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research framework
- PMID: 38978081
- PMCID: PMC11229258
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-024-01222-3
Implementation factors of tuberculosis control program in primary healthcare settings in China: a mixed-methods using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research framework
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is a major cause of death worldwide, and Chinese TB burden ranked the second globally. Chinese primary healthcare (PHC) sectors implement the TB Control Program (TCP) to improve active case finding, referral, treatment adherence, and health education. This study aimed to identify barriers and enablers of TCP implementation in high TB burden regions of West China.
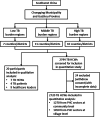
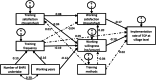
Methods: We conducted a representative study using mixed-methods in 28 counties or districts in Chongqing Municipality and Guizhou Province of West China from October 2021 to May 2022. Questionnaire surveys and semi-structured in-depth interviews were conducted with 2720 TB healthcare workers (HCWs) and 20 interviewees in PHC sectors. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to investigate TB HCWs' characteristics, and path analysis model was utilized to analyze the impact of associated factors on TCP implementation. Thematic framework analysis was developed with the guide of the adapted Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) on factors of TCP implementation.
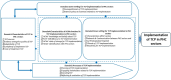
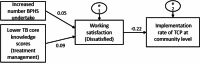
Results: This study found that 84.6% and 94.1% of community and village HCWs had low professional titles. Based on the results of multiple regression analysis and correlation analysis, lower TB core knowledge scores (-0.09) were identified as barriers for TCP implementation in community PHC sectors, and low working satisfaction (-0.17) and low working willingness (-0.10) are barriers for TPC implementation in village PHC sectors. The results of in-depth interviews reported barriers in all domains and enablers in four domains of CFIR. There were identified 19 CFIR constructs associated with TCP implementation, including 22 barriers such as HCWs' heavy workload, and 12 enablers such as HCWs' passion towards TCP planning.
Conclusions: With the guide of the CFIR framework, complex factors (barriers and enablers) of TCP implementation in PHC sectors of West China were explored, which provided important evidences to promote TB program in high TB burden regions. Further implementation studies to translate those factors into implementation strategies are urgent needed.
Keywords: Barriers and enablers; China; Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research; Implementation science; Primary setting; Tuberculosis control.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The job burnout of tuberculosis healthcare workers and associated factors under integrated tuberculosis control model: a mixed-method study based on the two-factor theory.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Aug 26;24(1):984. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11472-4. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39187887 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis treatment management in primary healthcare sectors: a mixed-methods study investigating delivery status and barriers from organisational and patient perspectives.BMJ Open. 2022 Apr 20;12(4):e053797. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053797. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35443945 Free PMC article.
-
Challenge of ending TB in China: tuberculosis control in primary healthcare sectors under integrated TB control model-a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 11;24(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16292-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38212753 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare workers' perspectives on the implementation of tuberculosis infection prevention and control policy in rural Papua New Guinea.Aust J Prim Health. 2025 May;31:PY24051. doi: 10.1071/PY24051. Aust J Prim Health. 2025. PMID: 40388564
-
What tuberculosis infection control measures are effective in resource-constrained primary healthcare facilities? A systematic review of the literature.Rural Remote Health. 2023 Mar;23(1):7175. doi: 10.22605/RRH7175. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Rural Remote Health. 2023. PMID: 36947945
Cited by
-
Current update on surgical management for spinal tuberculosis: a scientific mapping of worldwide publications.Front Surg. 2025 Jan 24;11:1505155. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1505155. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 39925700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2023. 2023. https://publichealthupdate.com/global-tuberculosis-report-2023/. Accessed 12 Dec 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. The End TB Strategy. 2014. https://www.who.int/tb/strategy/end-tb/en/.2015. Accessed 12 Dec 2023.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

