Unmet need in pulmonary hypertension-associated interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD): a clinician survey of real-world management of PH-ILD in Europe
- PMID: 38978553
- PMCID: PMC11228598
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00039-2024
Unmet need in pulmonary hypertension-associated interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD): a clinician survey of real-world management of PH-ILD in Europe
Abstract
Background: With no approved therapies for pulmonary hypertension (PH) associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD) in Europe, we surveyed clinician perceptions on PH-ILD management and unmet need to understand current real-world practices.
Methods: An online clinician survey on PH-ILD management was conducted in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK.
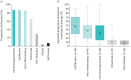
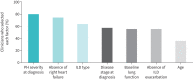
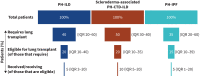
Results: 55 clinicians (78% pulmonologists), each managing a median 20 PH-ILD patients (interquartile range (IQR) 10-50), participated. Upon PH suspicion, clinicians referred a median 50% (IQR 20-73%) of patients for echocardiography alone and 35% (IQR 20-78%) for echocardiography, followed by right heart catheterisation. Upon diagnosis, a median 20% (IQR 9-30%), 40% (IQR 20-50%) and 35% (IQR 20-55%) of patients fell under the pulmonary arterial pressure ranges of 21-24 mmHg, 25-34 mmHg and >35 mmHg, respectively. 50% of patients received off-label treatment for their PH and, of those, off-label phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5i), endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) and prostacyclin analogues were prescribed first-line by 78%, 9% and 7% of clinicians, respectively. Upon PDE-5i non-response, 35% of clinicians proceed with an ERA, 35% with no further therapy. 55% of clinicians used dual-therapy. Yearly median inpatient admissions and emergency visits were 2.0 (IQR 1.3-2.9) and 1.5 (IQR 1.0-2.0), respectively (n=31 responses). Most clinicians (69%) highlighted lack of efficacy or evidence for current therapies as a key gap in PH-ILD management.
Conclusions: This study gives insight into real-world European PH-ILD diagnosis and management. With significant use of off-label treatment, there is a large unmet need due to lack of approved therapies. Despite updated guidelines, more evidence is needed to standardise PH-ILD management.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: S. Ghio, H. Nunes, J.M. Cifrián, R.P. Rojo and A. Guenther report no conflict of interest. D. Montani reports receiving grants and personal fees from Actelion, Bayer, GSK, Pfizer, MSD, Chiesi, Boehringer and Acceleron. F. Meloni reports having participated in advisory boards for Zambon and Boehringer. J. Cannon reports having received honorarium for attending and speaking at Janssen and Ferrer advisory boards and international conferences. L. Howard reports having received honoraria from Ferrer. H.G. García, M.F. Delgado and G.B. Jeanneret are employed by Ferrer Pharma Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Wijeratne DT, Lajkosz K, Brogly SB, et al. . Increasing incidence and prevalence of World Health Organization groups 1 to 4 pulmonary hypertension: a population-based cohort study in Ontario, Canada. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2018; 11: e003973. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.117.003973 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
