Tirzepatide against obesity and insulin-resistance: pathophysiological aspects and clinical evidence
- PMID: 38978621
- PMCID: PMC11228148
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1402583
Tirzepatide against obesity and insulin-resistance: pathophysiological aspects and clinical evidence
Abstract
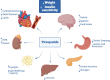
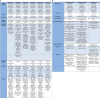
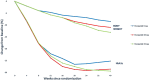
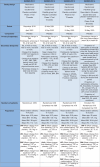
Obesity is a chronic, multifactorial disease in which accumulated excess body fat has a negative impact on health. Obesity continues to rise among the general population, resulting in an epidemic that shows no significant signs of decline. It is directly involved in development of cardiometabolic diseases, ischemic coronary heart disease peripheral arterial disease, heart failure, and arterial hypertension, producing global morbidity and mortality. Mainly, abdominal obesity represents a crucial factor for cardiovascular illness and also the most frequent component of metabolic syndrome. Recent evidence showed that Tirzepatide (TZP), a new drug including both Glucagon Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) and Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonism, is effective in subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D), lowering body weight, fat mass and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) also in obese or overweight adults without T2D. This review discusses the pathophysiological mechanisms and clinical aspects of TZP in treating obesity.
Keywords: GIP; GLP - 1; Tirzepatide; arterial hypertension; clinical trials; insulin-resistance; obesity; pathophysiology.
Copyright © 2024 Corrao, Pollicino, Maggio, Torres and Argano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
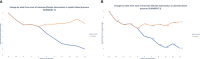
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Obesity . Available online at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity (Accessed 21 January 2024).
-
- Townsend N, Vogel C, Allender S, Halloran A, Sorensen K, John PH, et al. . WHO European Regional Obesity: Report 2022. Copenhagen: World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe; (2022).
-
- Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, De Gonzalez AB, et al. . Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet. (2016) 388:776–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30175-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

