Regulation of MAIT cells through host-derived antigens
- PMID: 38979423
- PMCID: PMC11228242
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424987
Regulation of MAIT cells through host-derived antigens
Abstract
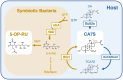
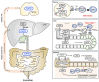
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a major subset of innate-like T cells that function at the interface between innate and acquired immunity. MAIT cells recognize vitamin B2-related metabolites produced by microbes, through semi-invariant T cell receptor (TCR) and contribute to protective immunity. These foreign-derived antigens are presented by a monomorphic antigen presenting molecule, MHC class I-related molecule 1 (MR1). MR1 contains a malleable ligand-binding pocket, allowing for the recognition of compounds with various structures. However, interactions between MR1 and self-derived antigens are not fully understood. Recently, bile acid metabolites were identified as host-derived ligands for MAIT cells. In this review, we will highlight recent findings regarding the recognition of self-antigens by MAIT cells.
Keywords: MAIT cell; MR1 ligand; T cell development; bile acids; self-antigen.
Copyright © 2024 Ito and Yamasaki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antigen Recognition by MR1-Reactive T Cells; MAIT Cells, Metabolites, and Remaining Mysteries.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 27;11:1961. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01961. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32973800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAIT cells and MR1-antigen recognition.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Jun;46:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 8. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28494326 Review.
-
MAIT, MR1, microbes and riboflavin: a paradigm for the co-evolution of invariant TCRs and restricting MHCI-like molecules?Immunogenetics. 2016 Aug;68(8):537-48. doi: 10.1007/s00251-016-0927-9. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Immunogenetics. 2016. PMID: 27393664 Review.
-
Mouse mucosal-associated invariant T cell receptor recognition of MR1 presenting the vitamin B metabolite, 5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-d-ribitylaminouracil.J Biol Chem. 2024 May;300(5):107229. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107229. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38537698 Free PMC article.
-
T cell receptor diversity, specificity and promiscuity of functionally heterogeneous human MR1-restricted T cells.Mol Immunol. 2021 Feb;130:64-68. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.009. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33360378 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

