Analysis of pediatric outpatient visits uncovers disparities in molluscum contagiosum treatment across medical specialties in the United States
- PMID: 38979519
- PMCID: PMC11228568
- DOI: 10.4081/dr.2023.9851
Analysis of pediatric outpatient visits uncovers disparities in molluscum contagiosum treatment across medical specialties in the United States
Abstract
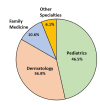
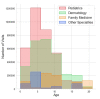
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a common viral infection that affects the skin of children. In this study, treatment regimens and demographic information for MC patients across US medical specialties were compared. We discovered an average of 471,383 pediatric MC visits annually using the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey database from 2000 to 2016. Non-Hispanics (82.9%) and Caucasians (91.0%) made up the majority of the visitors. The majority of cases were handled by pediatricians (46.5%), family medicine doctors (10.6%), and dermatologists (36.7%). Compared to pediatricians, dermatologists saw a higher percentage of Caucasian patients (95% vs.84%) and patients with private insurance (83% vs. 73%). Patients were more likely to see family medicine doctors (55.0%) in non-metropolitan areas than pediatricians (26.4%) or dermatologists (16.3%). Dermatologists were less likely than pediatricians (38%) to favor spontaneous resolution (70%). Dermatologists favored terpenoids (20%), imiquimod (12%), and curettage (10%), while pediatricians primarily used terpenoids (12%), steroids (4%), and imiquimod (4%). The majority of MC cases are managed by pediatricians; however, treatment approaches deviate markedly from recommended best practices.
Keywords: health disparities; molluscum contagiosum; pediatric dermatology; pediatric outpatient visits.
Copyright © 2024, the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen X, Anstey AV, Bugert JJ. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2013;13:877-88. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Piguet V, Francis NA. Epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children: a systematic review. Fam Pract 2014;31:130-6. - PubMed
-
- Tyring SK. Molluscum contagiosum: the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:S12-6. - PubMed
-
- Basdag H, Rainer BM, Cohen BA. Molluscum contagiosum: to treat or not to treat? Experience with 170 children in an outpatient clinic setting in the northeastern United States. Pediatr Dermatol 2015;32:353-7. - PubMed
-
- Lee R, Schwartz RA. Pediatric molluscum contagiosum: reflections on the last challenging poxvirus infection, Part 1. Cutis 2010;86:230-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

