Melanoma of the external auditory canal: case report and systematic literature review
- PMID: 38979587
- PMCID: PMC11447658
- DOI: 10.32074/1591-951X-980
Melanoma of the external auditory canal: case report and systematic literature review
Abstract
Melanoma of the external auditory canal (EAC) is particularly rare and poorly understood, with limited available data on management and survival. This systematic review aims to analyze existing data and provide insights into the management and prognosis the beginning of EAC melanoma. It is conducted using Pubmed and Scopus databases from the beginning to July 2023 and it follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Searches are performed using the search string "(melanoma) AND (external auditory canal)".
The review includes a total of 30 patients diagnosed with EAC melanoma, supplemented by an additional case from the authors' clinical experience. The role of Breslow thickness as a determining factor for the choice of surgery remains inconclusive due to limited available data. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and adjuvant therapy are sparingly employed, indicating the need for standardized guidelines. Patients in the study demonstrate a 50% overall survival rate at 5 years.
EAC Melanoma is a rare and aggressive malignancy with limited therapeutic guidelines. Surgical interventions, including wide local excision and lateral temporal bone resection, are the primary treatment options for patients without distant metastases.
Keywords: ear’s melanoma; external auditory canal; melanoma; skull base surgery; surgery for melanoma.
Copyright © 2024 Società Italiana di Anatomia Patologica e Citopatologia Diagnostica, Divisione Italiana della International Academy of Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
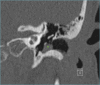
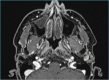


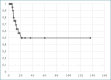
References
-
- PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Melanoma treatment (PDQ®): health professional version. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2002. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK66034/. Accessed March 7, 2019.
-
- Appelbaum EN, Gross ND, Diab A, et al. . Melanoma of the External Auditory Canal: A Review of Seven Cases at a Tertiary Care Referral Center. Laryngoscope. 2021;131(1):165-172. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28548 10.1002/lary.28548. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Byers RM, Smith JL, Russell N, et al. . Malignant melanoma of the external ear. Review of 102 cases. Am J Surg 1980;140:518-521. - PubMed
-
- Hawkes JE, Truong A, Meyer LJ. Genetic predisposition to melanoma. Semin Oncol 2016;43:591-597. - PubMed
-
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. . The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021. Mar 29;372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 10.1136/bmj.n71. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

