Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine in Asian patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 38979893
- PMCID: PMC11462951
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16234
Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine in Asian patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
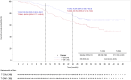
The global phase 3 DESTINY-Breast03 study (ClinicalTrials.gov; NCT03529110) showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) over trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer (mBC) previously treated with trastuzumab and a taxane. Here, we report a subgroup analysis of Asian patients enrolled in DESTINY-Breast03. In total, 309 patients (149 in the T-DXd arm and 160 in the T-DM1 arm) from Asian countries and regions were randomized. At data cutoff (July 25, 2022), the median duration of follow-up in the Asian subpopulation was 29.0 months with T-DXd and 26.0 months with T-DM1. The PFS (determined by blinded independent central review) hazard ratio was 0.30 (95% confidence interval 0.22-0.41) favoring T-DXd over T-DM1 (median PFS 25.1 vs. 5.4 months). Median OS was not reached in the T-DXd arm and was 37.7 months in the T-DM1 arm. The median treatment duration was 15.4 months with T-DXd and 5.5 months with T-DM1. The incidence of grade ≥3 drug-related treatment-emergent adverse events was similar between both treatment arms (49.0% vs. 46.5%) and was consistent with the overall DESTINY-Breast03 population. Adjudicated drug-related interstitial lung disease or pneumonitis occurred in 12.9% of patients treated with T-DXd and 2.5% treated with T-DM1, with a higher incidence in Japanese patients; none of these were grade ≥4 events. These efficacy and safety data reinforce the favorable benefit-risk profile of T-DXd in HER2-positive mBC, including in the Asian subgroup.
Keywords: East Asia; ErbB‐2 receptor; breast cancer; trastuzumab deruxtecan; trastuzumab emtansine.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Hiroji Iwata received lecture fees or honoraria from AstraZeneca, received research funds from AstraZeneca and Pfizer, and is an editorial board member of
Figures


References
-
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance EaERP . Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer subtypes. 2023. NIH, Seer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast‐subtypes.html. Accessed 14 November 2023
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

